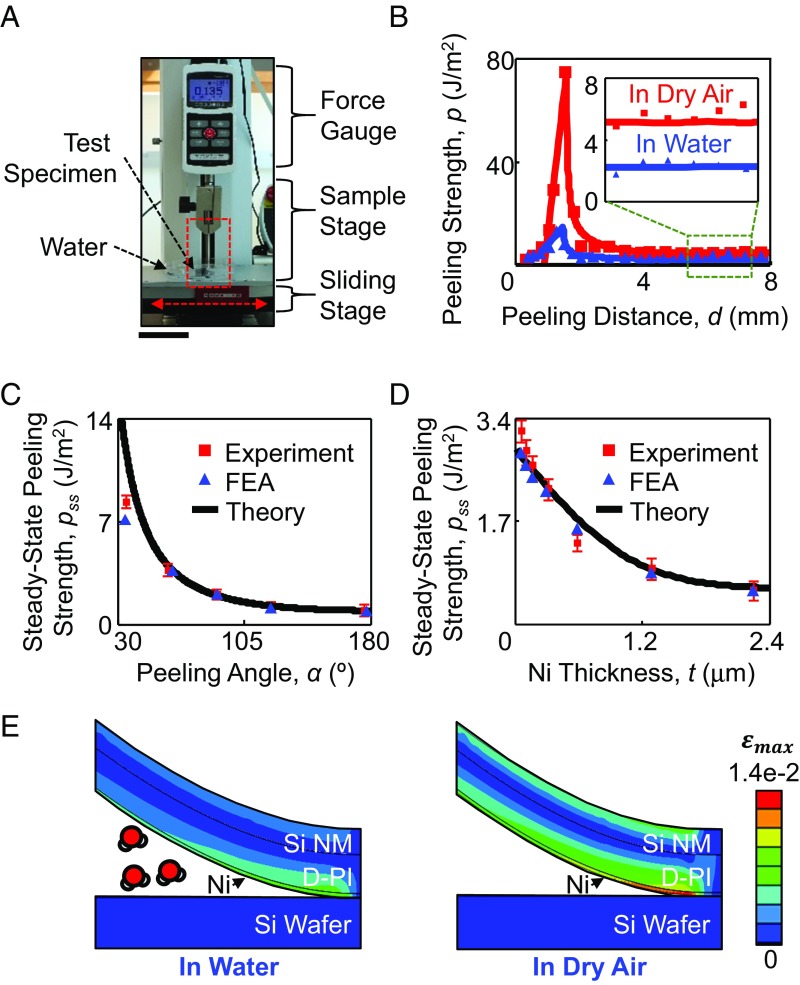
Fig. 2.
(A) An optical image of a custom-modified mechanical peeling apparatus. (Scale bar: 6 cm.) (B) Experimental (dots) and finite-element analysis (FEA, lines) results of peeling strength as a function of peeling distance in water and dry air conditions. The Inset shows a magnified view of the peeling strength–distance curves at steady-state stage. (C) Experimental, FEA, and theoretical results of the steady-state peeling strength in water with varied peeling angles from 30° to 180°. (D) Experimental, FEA, and theoretical data of steady-state peeling strength in water with varied Ni thickness from 30 nm to 2.4 μm. (E) FEA results of maximum principal strain distributions in the thin films under mechanical peeling in water (Left) and dry air conditions (Right).