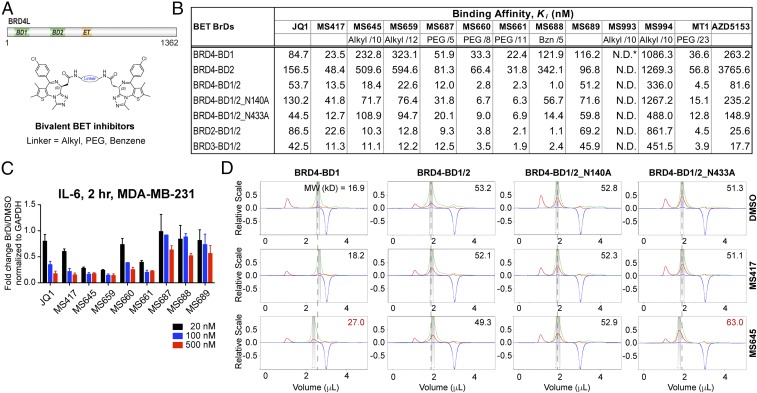
Fig. 1.
Biophysical characterization of bivalent BrD inhibition of the BET proteins. (A) Domain organization of BRD4 and depiction of bivalent BET inhibitors. (B) Binding affinity of BrD inhibitors to BET BrD proteins as determined by an FP assay. The BET BrD proteins used are BRD4-BD1 (amino acids 44–168), BRD4-BD2 (amino acids 347–460), BRD4-BD1/2 (amino acids 44–477), BRD4-BD1/2_N140A (amino acids 44–477), BRD4-BD1/2_N433A (amino acids 44–477), BRD2-BD1/2 (amino acids 73–473), and BRD3-BD1/BD2 (amino acids 24–434). The chemical composition and length (depicted by number of atoms) for the linker are indicated for bivalent BET inhibitors. (C) Dose-dependent effects of BET inhibitors on transcriptional expression of IL-6 in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with the BrD inhibitors as indicated for 2 h. Results represent at least three independent experiments and error bars denote SEM. (D) Effects of BrD inhibitor binding on protein conformation of BRD4 BD1 alone or tandem BD1/BD2, as assessed by aMW of the protein determined by DLS. Measurements of UV, scattering intensity, and refractive index change are color-coded in green, red, and blue, respectively.