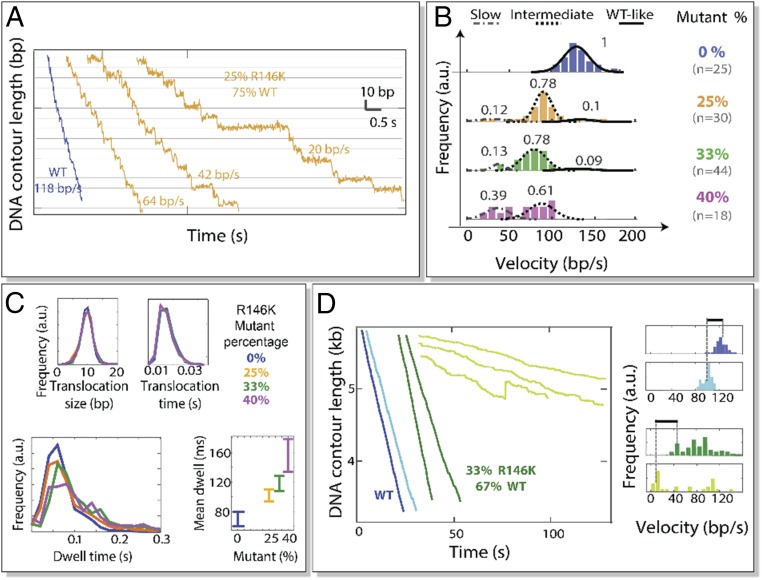
Fig. 3.
Packaging behavior of R146K/WT hybrid motors. (A) High-resolution packaging trajectories with WT (blue) and R146K/WT hybrid rings (gold). (B) Velocity distribution of R146K/WT mixtures for different mixing ratios. Each velocity group was fitted to a Gaussian distribution. The Gaussians were normalized within each mixing condition to represent the fraction of motors belonging to each group (SI Appendix has a detailed analysis). (C) Analysis of the dwell and translocation phases of R146K/WT hybrid rings (25, 33, and 40% mutant) and the WT (0% mutant). (D) ADP inhibition experiments. (Left) Sample packaging trajectories for WT (blue) and R146K/WT hybrid motors (green) and in the presence of ADP (light blue and light green, respectively; [ATP] = [ADP] = 500μM). (Right) Velocity distribution of WT and R146K/WT hybrid rings in the presence and absence of ADP (same color code as in Left). Dotted lines correspond to the mean packaging velocity. Black lines on top indicate the extent of inhibition by ADP in either scenario.