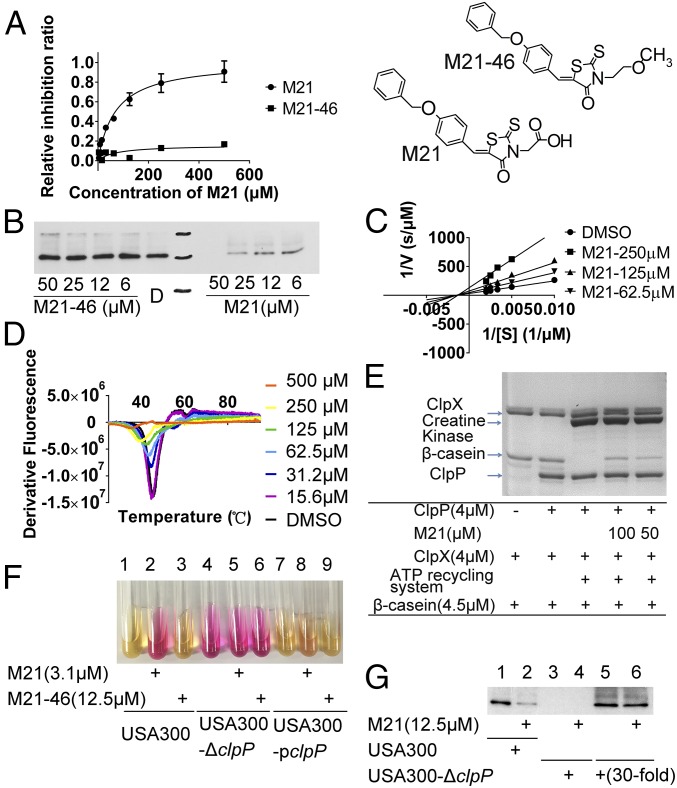
Fig. 2.
M21 Binds to and Inhibits ClpP Activity. (A) M21 inhibits ClpP cleavage of SUc-LY-AMC substrate in a peptidase assay. Concentrations of ClpP and Suc-LY-AMC used were 1 μM and 100 μM, respectively. (B) Western blotting analysis of a-toxin production altered by M21 and its analog. (C) Noncompetitive inhibition of M21 on ClpP cleavage of Suc-LY-AMC. M21 increased the maximum velocity (Vmax), but did not affect the Michaelis constant (Km) of ClpP enzyme reactions. (D) Differential scanning fluorimetry analysis of the binding between different concentrations of M21 and ClpP. The ClpP became instable to heat with the presence of M21. (E) Proteolytic assay confirming M21 protect β-casein from degradation by ClpP/ClpX. (F) Urease production in USA300 was induced by M21, but not M21-46. Overexpression of ClpP lead to the resistance of USA300 to M21-induced urease production. (G) Western blot analysis of the production of α-toxin in wild-type strain and clpP deleted strain. M21 showed no repression effect on the production of α-toxin when clpP was deleted.