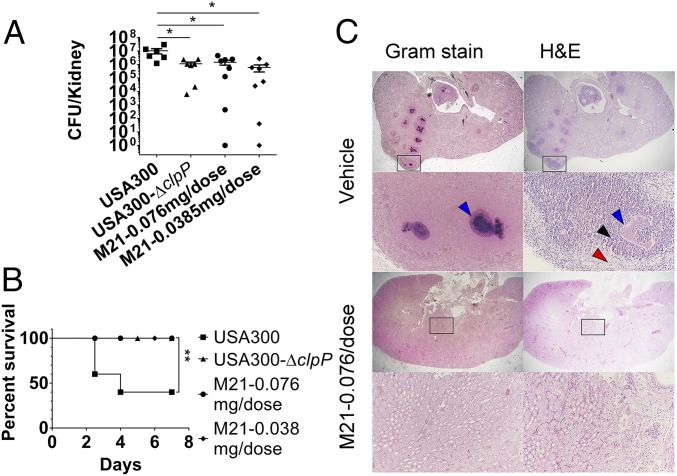
Fig. 5.
M21 reduces S. aureus pathogenicity in mouse model of intravascular infection. (A) Bacterial load of S. aureus USA300 or USA300-∆clpP in the kidney of mice after i.v. infection in the presence or absence of M21 treatment. (B) Bacteremia lethal model on mice with infection of S. aureus USA300 and USA300-∆clpP in the presence or absence of M21 treatment. (C) Histopathology of staphylococcal abscess communities. BALB/c mice were infected with S. aureus Newman via retro-orbital injection. Gram-stained and H&E-stained tissues of infected kidneys on day 10 after infection were analyzed by light microscopy, and images were captured. In the graph, each dot represents a mouse. The group treated with injection buffer is indicated as ‘‘Vehicle.’’ The group treated with compound M21 is indicated as ‘‘M21.’’ The statistical difference was calculated by Student’s two-tailed t test. Survival data were calculated by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. All data represent mean values ±SEM (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). P values were determined using GraphPad Prism, using an unpaired parametric t test with Welch’s correction and log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.