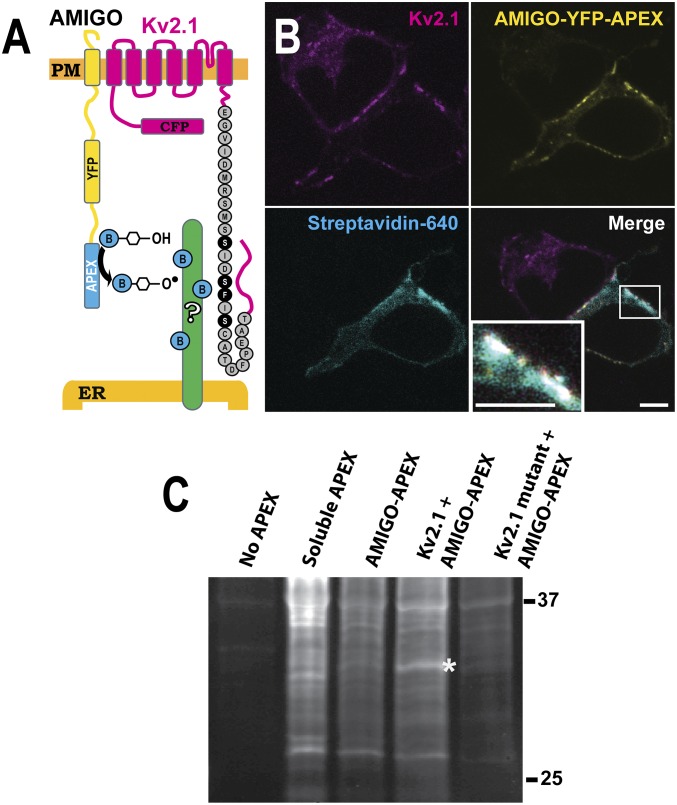
Fig. 1.
Use of proximity biotinylation to identify potential Kv2.1 interactors. (A) Diagram of the approach. APEX was attached to the C-terminal end of the Kv2.1 beta subunit, AMIGO. (B) Localization of APEX-mediated biotinylation. HEK cells were transfected with Kv2.1 and AMIGO-YFP-APEX, treated with biotin and H2O2, and then fixed using formaldehyde and labeled with CF640R-conjugated streptavidin to visualize biotinylated proteins as imaged with a laser scanning confocal microscope. Biotinylation localized at ER/PM junctions occurs only in cells expressing AMIGO-YFP-APEX and Kv2.1 (see Lower Right Inset for an enhanced view of biotinylation at a Kv2.1 cluster). (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (C) Parallel samples were collected and subjected to Western blot analysis without affinity purification, using streptavidin–horse radish peroxidase to visualize all biotinylated proteins. A 33-kDa band is present when AMIGO-YFP-APEX is coexpressed with the WT Kv2.1 channel (asterisk). This band is absent from the indicated control lanes, i.e., without any APEX transfection, with soluble APEX expression, and when AMIGO-YFP-APEX is expressed alone or expressed with a mutant Kv2.1 channel which is unable to form ER/PM junctions.