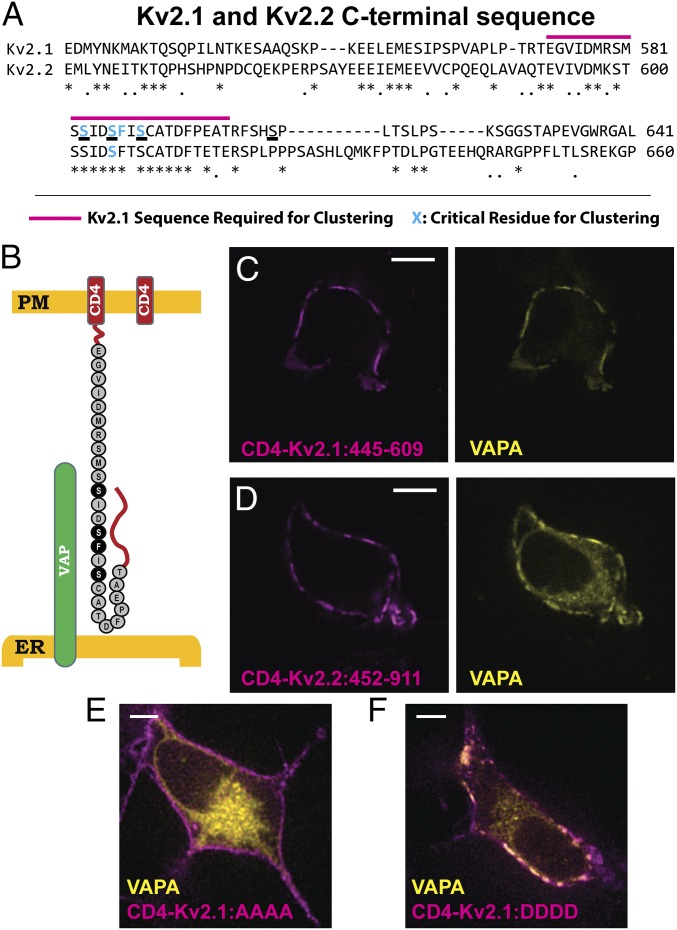
Fig. 6.
Kv2 channel C terminus is sufficient to form ER/PM junctions through VAP interaction. (A) Sequence comparison of Kv2.1 and Kv2.2 C termini. Note the high degree of conservation in the area required for clustering, but lack thereof elsewhere. Known sequence required for clustering in Kv2.1 is indicated by the magenta line. Known amino acids required for clustering are highlighted in cyan. (B) Schematic of WT CD4, on right, and the CD4-Kv2.1:445–609 construct, on left. Critical amino acids for Kv2.1 clustering are included in black. (C) Appending amino acids 445–609 of Kv2.1 onto the CD4 C terminus results in ER/PM junctions that concentrated VAPA at the PM. (D) The C terminus of Kv2.2 attached to CD4 also results in a construct that clusters and interacts with VAPs. (E) Expression of VAPA-GFP with the CD4-Kv2.1:445–609 construct in which the serines underlined in A were mutated to alanines. (F) Expression of VAPA-GFP with the CD4-Kv2.1:445–609 construct in which the serines underlined in A were mutated to aspartic acids. (Scale bars: 5 µm.)