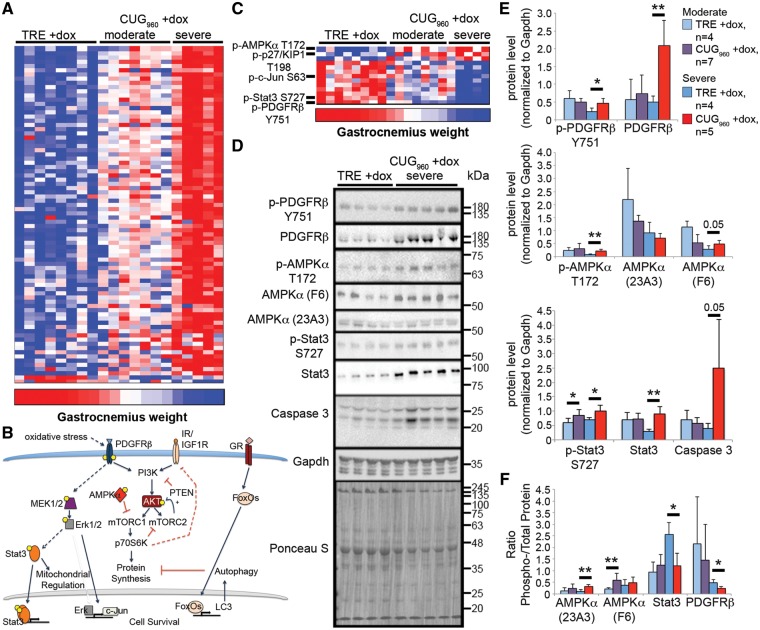
Figure 6.
Signaling pathway analysis reveals deregulation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. (A) RPPA analysis was performed using total protein lysates from female gastrocnemius muscle with 216 validated antibodies. Normalized fluorescence intensity, grouped according to muscle wasting severity (severe gastrocnemius weight <56 mg, moderate gastrocnemius weight 60–76 mg, control gastrocnemius weight >79 mg, P≤0.001), showed predominantly increased protein expression in CUG960 +dox mice with severe muscle wasting. (B) The PTEN/PI3K, IL-8, and glucocorticoid signaling pathways were the most significantly altered pathways in CUG960 mice. (C) Analysis of the ratio of phosphorylated to total protein level suggests that in CUG960 +dox mice with severe muscle wasting, the PTEN/PI3K pathway antagonist AMPKα is significantly increased while activated PDGFRβ receptor, known to activate PI3K, and activated Stat3, downstream of PDGFRβ, were reduced. (D) Validation by western blot analysis in female gastrocnemius muscle extracts of severely affected animals. (E) Quantification of western blots shown in (D). (F) Quantification of phospho- to total protein ratios for western blots in (D). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.