Table 2.
Schematic representations of the reviewed incorporation strategies and their resulting growth factor release profiles
| Incorporation strategy | Schematic | Release profile [72] | Advantages (+) and limitations (−) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Covalent binding | 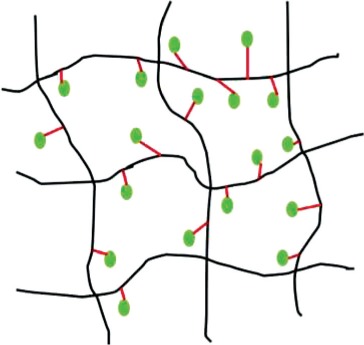 |
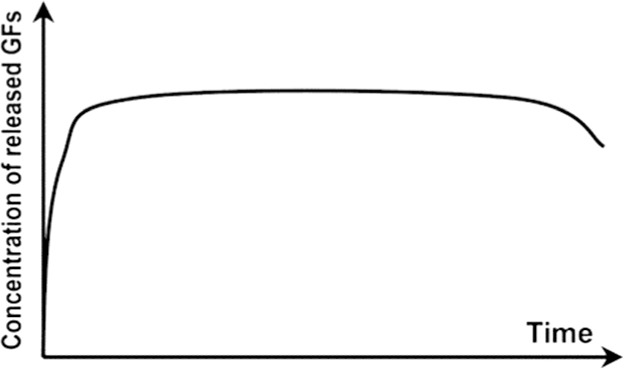 |
|
| Physical entrapment/ Adsorption | 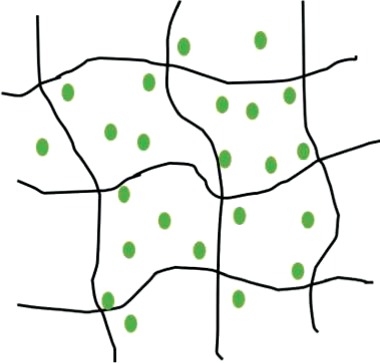 |
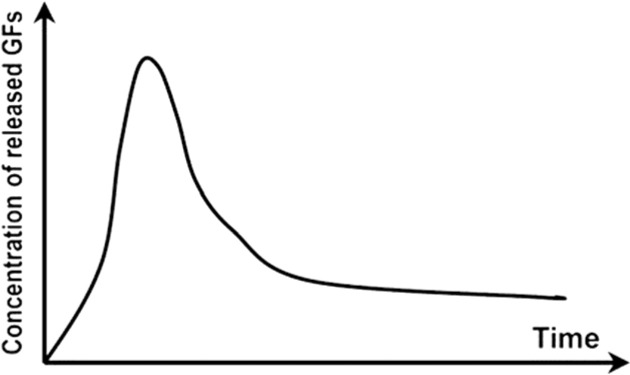 |
|
| Incorporation into micro/nanospheres | 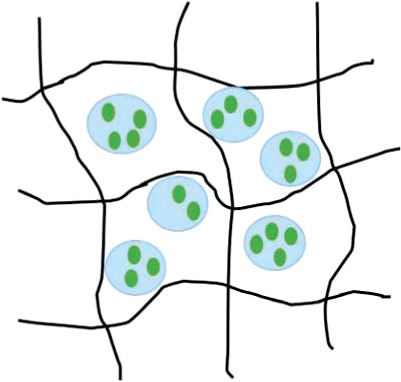 |
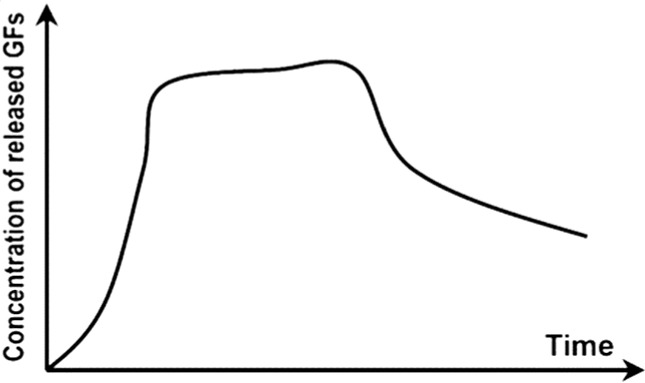 |
|
 = covalent bond;
= covalent bond;  = growth factor;
= growth factor;  = micro/nanocapsule.
= micro/nanocapsule.
