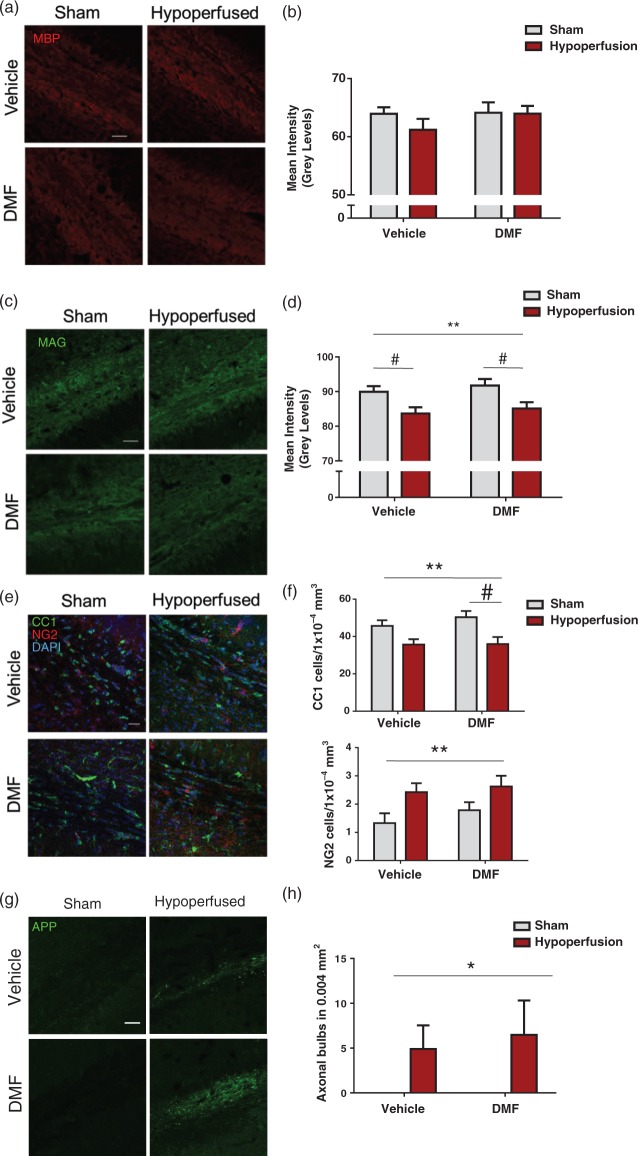
Figure 5.
Axon-glial integrity was damaged by severe hypoperfusion but unaffected by DMF administration. (a) Confocal images from the corpus callosum of animals from four experimental groups immunostained with MBP (red), scale bar: 50 µm. (b) Quantification of MBP immunostaining sections showing no significant changes in myelin among the groups. (c) Confocal images from the corpus callosum of animals from four experimental groups immunostained with MAG (green), scale bar: 50 µm. (d) MAG immunostained sections showing changes in myelin in hypoperfused animals. Quantification of MAG mean intensity shows an overall significant effect of surgery (F(1-31) = 11.7; **p = 0.002) Post hoc comparison shows a significant reduction with hypoperfusion in both vehicle (#p < 0.05) and DMF treated (#p < 0.05) groups. (e) Confocal images from the corpus callosum from four experimental groups immunostained for markers of mature oligodendrocytes (CC1) and oligodendrocyte precursor cells (NG2). Green: CC1; red: NG2, blue: DAPI, scale bar: 100 µm. (f) There is a significant reduction in the number of CC1 cells following hypoperfusion (F(1-33) = 13.0; **p = 0.001) Post hoc comparison shows a significant reduction in the number of CC1 immunopositive cells following hypoperfusion in DMF-treated mice (#p < 0.05) but not in vehicle-treated mice (#p > 0.05). There was significant increase in NG2-positive cells following hypoperfusion surgery (F(1-33) = 7.6; **p = 0.009). (g) APP-immunostained sections showing axonal damage in hypoperfused animals while minimal immunostaining is detected in shams. Green: APP. Scale bar: 50 µm. (h) Quantification of axonal bulbs shows an overall significant effect of surgery (F(1-33) = 4.9; *p = 0.04). Data presented as mean ± SEM, Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, sham vehicle n = 7; sham DMF n = 8; hypoperfusion vehicle n = 13; hypoperfusion DMF n = 9.