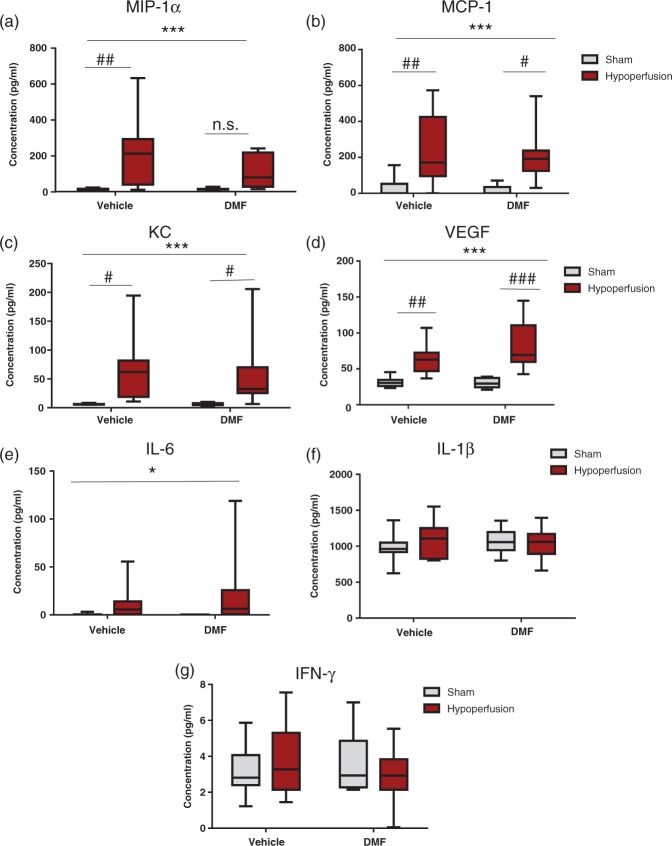
Figure 7.
The effect of DMF on chemokines, growth factors and cytokines. Levels of inflammatory-related proteins were calculated (pg/ml) using a multiplex assay. (a) There was a highly significant effect of surgery (F (1-34) = 13.7; ***p = 0.0008) in the concentration of MIP-1α (pg/ml). Post hoc analysis showed that there was a significant increase in MIP-1α levels in hypoperfused vehicle-treated animals compared with sham vehicle-treated animals (##p < 0.01); however, notably there was no significant increase in MIP-1a levels in the DMF-treated hypoperfused mice compared with the DMF-treated sham mice (p > 0.05). (b) There was a highly significant effect of surgery (F (1-34) = 18.2; ***p = 0.0001) in the concentration of MCP-1 (pg/ml). Post hoc analysis showed that there was a significant increase in MCP-1 levels in hypoperfused vehicle-treated animals compared with sham vehicle-treated animals (##p < 0.01) and a significant increase in MCP-1 levels in hypoperfused DMF-treated animals compared with sham DMF-treated animals, but by a lesser magnitude (#p < 0.05). (c) There was a significant effect of surgery (F (1-33) = 14.3; ***p = 0.0006) in the concentration of KC (pg/ml). Post hoc analysis showed that there was a significant elevation in KC levels following hypoperfusion vehicle compared with sham vehicle treatment (#p < 0.05), and in hypoperfused DMF-treated mice when compared with sham DMF-treated mice (#p < 0.05). (d) There was a highly significant effect of surgery (F (1-34) = 34.8; ***p < 0.0001) in the concentration of VEGF (pg/ml). Post hoc analysis showed that there was a significant increase in VEGF levels in hypoperfused vehicle-treated animals compared with sham vehicle-treated animals (##p < 0.01). Notably, there was also a significant increase in VEGF levels in the DMF-treated hypoperfused mice compared with the DMF-treated sham mice, by a greater magnitude (###p < 0.001) than the increase seen in vehicle treated mice. (e) For IL-6 levels, there was a significant effect of surgery (F (1-34) = 4.4, *p = 0.04). (f and g) There was no significant effect of hypoperfusion or DMF for IL-1β (f) or for IFN-γ (g). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, sham vehicle n = 8; sham DMF n = 8; hypoperfusion vehicle n = 11; hypoperfusion DMF n = 11.