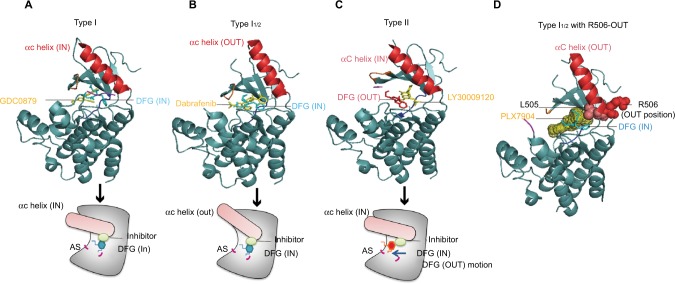
Figure 2.
The crystal structure of different types of RAF inhibitors binding to BRAF kinase.
Notes: (A) The DFG motif (magnesium-binding site) is located at the N-lobe base of the AS, and the type I inhibitor (GDC0879) binding to BRAF displays the DFG motif of BRAF maintaining the “IN” position, as well as the αC helix (PDB ID: 4MMF). (B) The type I1/2 inhibitor (dabrafenib) binds to BRAF and stabilizes the αC helix in the “OUT” position, and the position of the DFG motif remains in the IN position (PDB ID: 4XV2). (C) The structure of a type II inhibitor (LY3009120)-binding BRAF shows the different DFG motif positions, and the DFG motif shows the OUT motion compared with the BRAF crystal structure binding with type I or I1/2 RAF inhibitors (PDB ID: 5C9C). (D) The IN position of the residue R506 of the αC helix associates with the interaction of RAF with RAS-GTP. PLX7940 is a type I1/2 RAF inhibitor, and except the αC helix OUT and DFG motif IN positions of BRAF, the residue R506 in the αC helix displays an outward movement upon binding of the type I1/2 RAF inhibitor, which reduces the paradoxical activation of ERK signaling.
Abbreviations: AS, activation segment; PDB, Protein Data Bank.