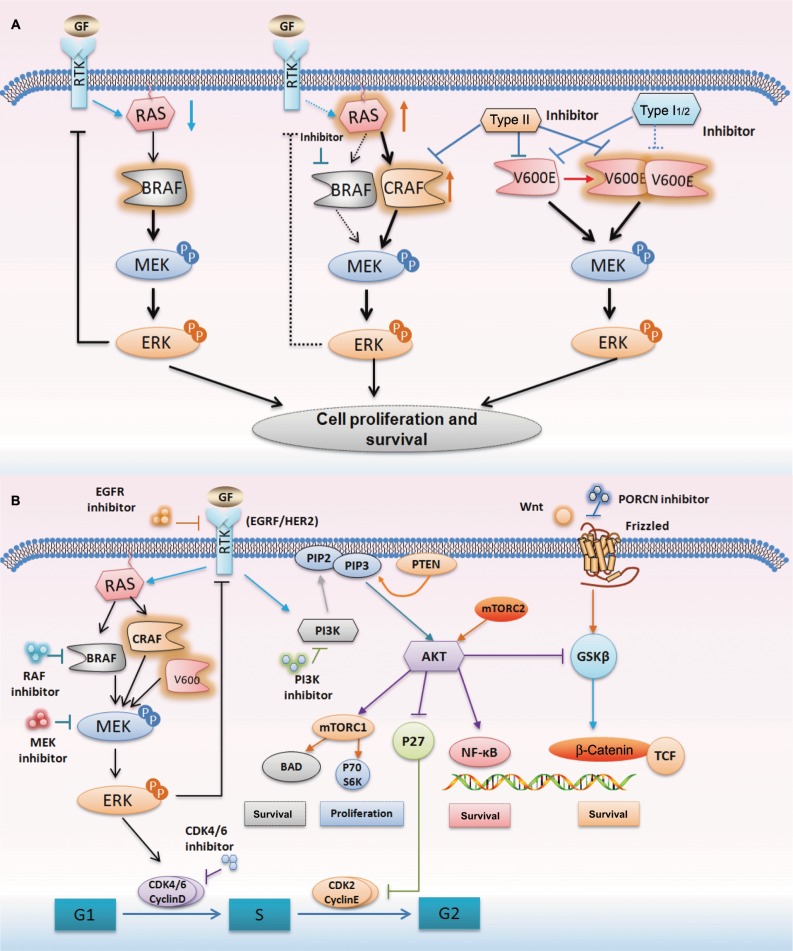
Figure 3.
The mechanism of feedback reactivation following BRAF inhibition and current combinatorial therapeutic targets.
Notes: (A) The activation of BRAF drives downstream MAPK signaling, and the activation of ERK leads to negative feedback on RTK activation and reduces RAS activity. When BRAF is suppressed by inhibitors, the ERK feedback is reduced and the activation of RAS is enhanced. RAS activates CRAF, inducing reactivation of the MAPK signaling. However, BRAF with the V600E mutant can drive high levels of ERK signaling output independently. Type II inhibitors can inhibit not only BRAF and CRAF but also BRAF with V600E mutant. (B) Outline of current combinatorial therapeutic targets based on the MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. These pathways have been identified as a mechanism of resistance to BRAF inhibitors.
Abbreviation: RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase.