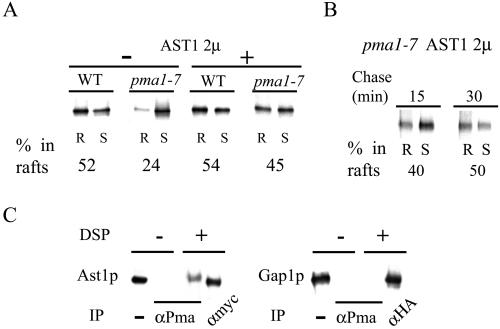
Figure 6.
AST1 overexpression restores raft-association of mutant ATPase. (A) Raft association of ATPase in WT (L3852) and pma1-7 (ACY7) cells at 24°C. ATPase raft association, with and without high copy AST1 (pAC49), was determined after radiolabeling and immunoprecipitation from TX100 containing density gradients as before. (B) Mutant ATPase raft association in the presence of high copy AST1. pma1-7 (ACY7) cells harboring the pAC49 plasmid were radiolabeled for 10 min at 24°C and chased for 15 or 30 min at 24°C. Raft association of newly synthesized ATPase was determined as in A. (C) Protein–protein interaction between Ast1p and Pma1p. WT (L3852) cells expressing epitope-tagged AST1 (pAC64) grown at 24°C were lysed and incubated on ice with or without the cross-linker DSP for 2 h. Ast1p was immunoprecipitated with a rabbit polyclonal anti-myc antibody or coimmunoprecipitated with anti-Pma1p antibodies and subsequently detected with a mouse monoclonal anti-myc antibody. Ast1p is coimmunoprecipitated with Pma1p after treatment with DSP, the slightly lower mobility of Ast1p is probably due to cross-linking. Cells expressing Gap1-HA were grown in media containing urea as nitrogen source and subjected to the same procedure. Gap1-HA was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA–tag rabbit polyclonal antibodies or with anti-Pma1p antibodies and subsequently detected with a mouse monoclonal anti-HA–tag antibody.