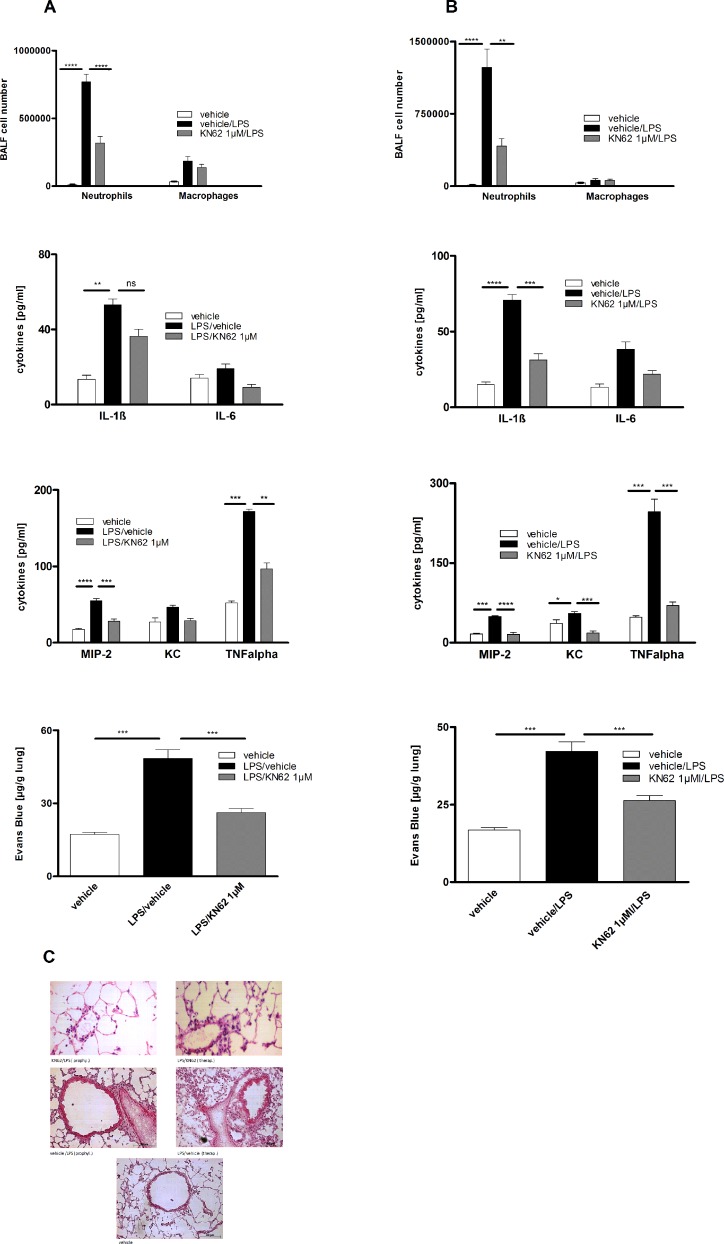
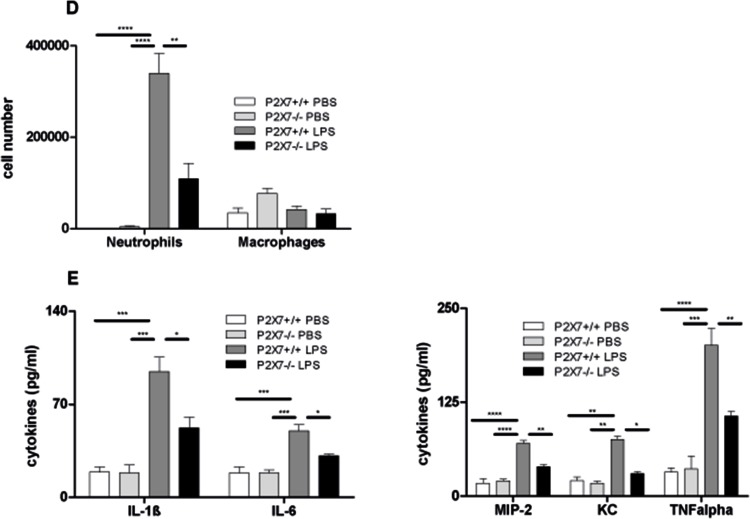
Figure 4. Effect of prophylactic or therapeutic administration of 1 µM KN62 and P2X7R-deficiency on LPS-induced ALI.
BALF cell differential count measured by flow cytometry. Concentration of IL-1ß, IL-6, KC, MIP-2 and TNF-α in BALF determined by ELISA. Plasma leakage determined spectrophotometrically 18 h after Evans blue dye albumin (20 mg/kg) was injected into the tail vein. (A) Therapeutic administration of 1 µM KN62 resulted in a non-significant reduction of BALF-cells, but in a significant decrease of cytokine levels (IL-1ß, MIP-2 and TNF-α) and a significant reduction in microvascular plasma leakage. (B) Prophylactic administration of 1 µM KN62 resulted in a significant reduction only of BALF-neutrophils and a decrease of cytokine levels (significant reduction for MIP-2 and TNF-α) as well as a significant reduction in microvascular plasma leakage. (C) Histology from lungs with therapeutically or prophylactically treated animals compared with untreated animal lungs showing reduced signs of ALI. (D and E) Wild-type and P2X7R−/− mice were left either untreated or exposed to LPS. Compared to wild-type P2X7R−/− mice exhibit a significant reduction of neutrophils in BALF (D) and all analyzed cytokine levels (IL-1ß, IL-6, MIP-2, KC, and TNF-α) (E). One representative experiment out of three is shown. Values are given as mean ± SEM. n = 5 mice in each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle/LPS.