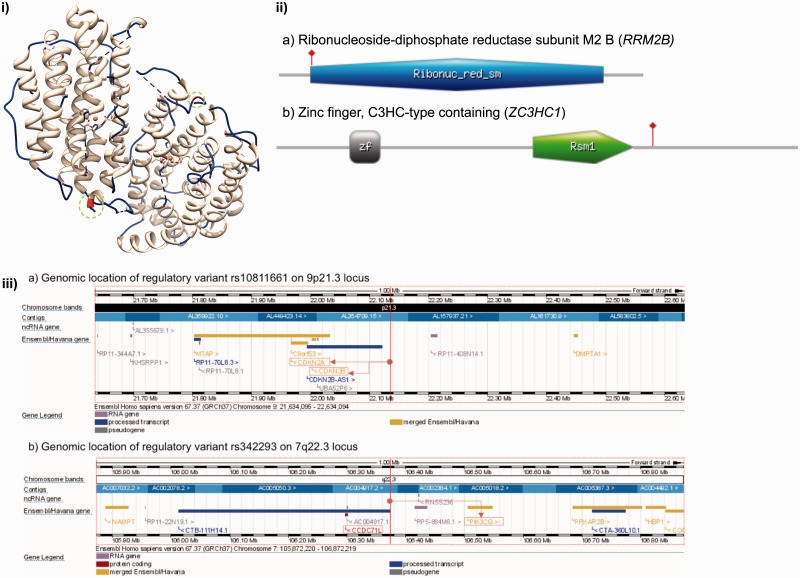
Figure 2.
Examples of the coding (functional) and noncoding (regulatory) variants. (i) Functional variant (Pro33Ser) in RRM2B associated with autosomal recessive progressive external ophthalmoplegia visualized on a protein structure (PDB ID: 2vux; Quaternary assembly is generated using PISA/PDBe). Functional variant (Pro33Ser) is highlighted in red color inside the green circle on chains A (part of loop) and B (part of helix). Visualization was created using UCSF Chimera ( www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera ). (ii) Protein domain architectures and functional variants mapped to ii (a) RRM2B and ii (b) ZC3HC1. Ribonuc_red_sm = Ribonucleotide reductase domain; zf = C3HC zinc finger-like domain; Rsm1 = Rsm1-like domain. Functional variants are highlighted using red vertical line. Figure was generated using MyDomains ( http://prosite.expasy.org/mydomains/ ). (iii) Genomic localization of the regulatory variants (a) rs10811661 and (b) rs342293. The location of the variants are highlighted using a vertical red line. Regulatory variant rs10811661 regulated the expression of nearby genes CDKN2A and CDKN2B (highlighted in red boxes). Intergenic variant rs342293 located between FLJ36031 (CCDC71L)-PIK3CG is located in a TFBS of EVI1 that regulates the expression (repress) of PIK3CG. Genomic regions were visualized using Ensembl Genome Browser v. 67.