Fig. 3.
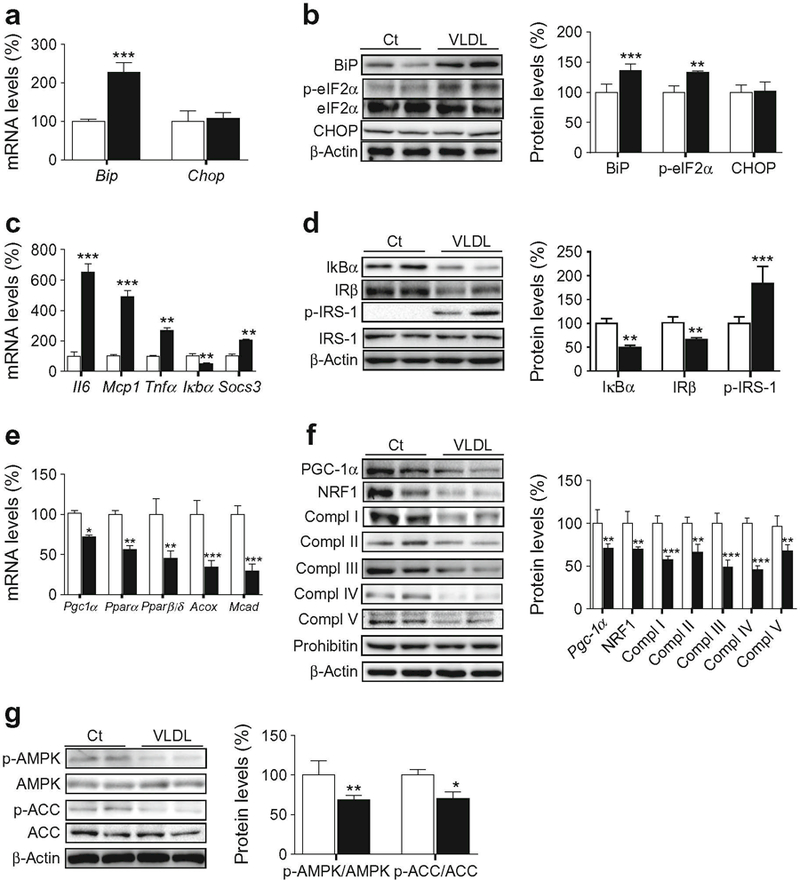
VLDL induces ER stress and inflammation, reduces the levels of mitochondrial proteins and attenuates the insulin signalling pathway in isolated skeletal muscle. Mouse gastrocnemius muscles were incubated in the presence (black bars) or absence (control, Ct, white bars) of 500 μg/ml VLDL for 6 h. (a) mRNA abundance of Bip and Chop. (b) BiP, PhosphoeIF2α (Ser51), CHOP and β-actin protein levels. (c) mRNA abundance of Il6, Mcp1, Tnfα, Iκbα and Socs3. (d) IκBα, IRβ, phospho-IRS-1 (Ser307), and β-actin protein levels. (e) Pgc1α, Pparα, Pparβ/δ, Acox and Mcad mRNA levels. (f) PGC-1α, NRF1, OXPHOS complexes (Compl), prohibitin and β-actin protein levels. (g) Phospho-AMPK (Thr172), phospho-ACC (Ser79) and β-actin protein levels. The graphs show quantification expressed as a percentage of control. Data are means ± SD of five independent experiments and were compared by Student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 and vs control
