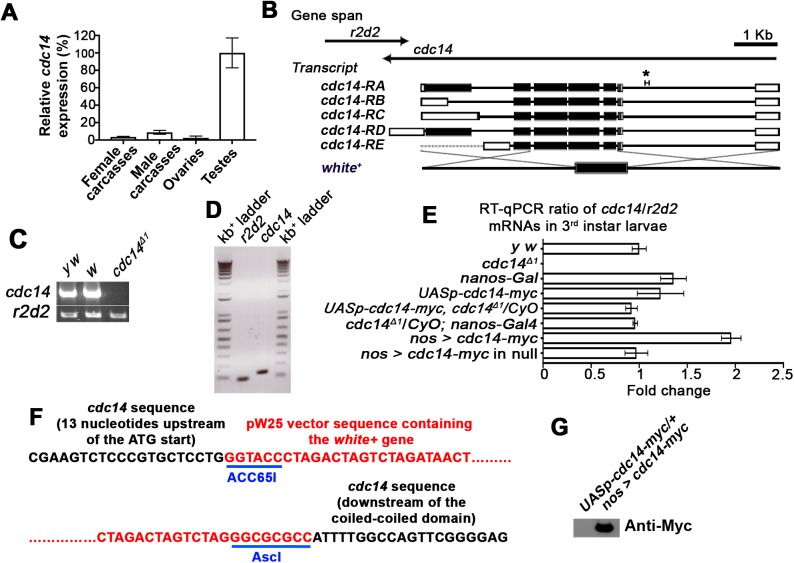
Fig. 1.
High expression of cdc14 in the testes and generation of Drosophila cdc14 null mutants by homologous recombination. (A) Relative expression of endogenous cdc14 in adult flies as determined by RT-PCR. The highest level of expression is in the testes. cdc14 expression was normalized to Rp49. cDNA was generated from adult carcasses (n≥50) or excised gonads (n≥200, n=3 independent biological replicates with n=3 technical replicates). (B) Structure of the Drosophila cdc14 and its five alternative transcripts. Black boxes are exons, white boxes are UTRs, and lines are introns. Ends-out homologous recombination of cdc14 was used to replace cdc14 with the white+ gene. Asterisk (*) indicates the 371 bp (2L:7,807,273 to 7,87,543) region of cdc14 used for PCR depicted in C. A region (2 kb; not shown) of the overlapping housekeeping gene, r2d2, was used as a positive PCR control. Control r2d2 PCR product is 2 kb. r2d2 is upstream of cdc14 (PCR region not depicted). White+ gene is not to scale. (C) A cdc14 null line was generated in a y w background and verified by PCR amplification of genomic DNA. The control lines, y w and w1118, and the adjacent housekeeping gene, r2d2, were used as positive controls. The cdc14Δ1 null allele was used for all subsequent experiments and for generation of the rescue line. The gel is a representative result from n=3 replicates. (D) Final products from the RT-qPCR reaction of y w third instar larvae run on a 1% agarose DNA gel. Only a single product was amplified, suggesting high specificity of the primers used in E. (E) Fold changes of cdc14 mRNA normalized to r2d2 mRNA. The level of expression is normalized to the y w control. No cdc14 expression was detectable in the cdc14 null line, but r2d2 expression was equivalent to that of the y w control line. cDNA was generated from late third instar larvae (n≥30, n=3 independent biological replicates with n=3 technical replicates). (F) Nucleotide sequence of the boundaries of the cdc14 null mutation. Two of the restriction endonuclease sites (ACC65I and AscI) used for cloning the two homologous arms of cdc14 into the pW25 vector for recombination are shown. (G) Anti-Myc immunoblot of 0–2 h old embryos demonstrates expression of UASp-cdc14-myc using the nanos-Gal4 driver.