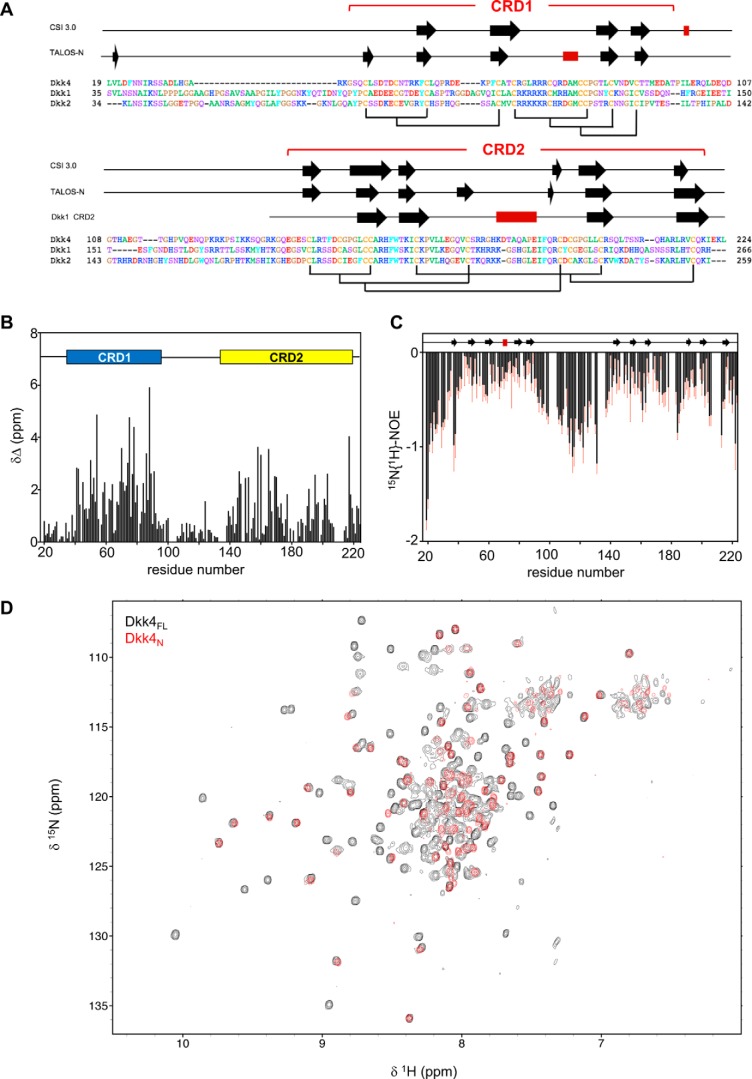
Figure 1.
Structural properties and features of full-length Dkk4. A, sequence alignment of mature human Dkk proteins obtained using Clustal O, with residues numbered from the N-terminal methionine. Indicated above are the regular secondary structure elements predicted from backbone NMR assignments obtained for Dkk4FL using CSI 3.0 and TALOS-N, with β-strands and α-helices represented by black arrows and red rectangles, respectively. The secondary structure observed for Dkk1 CRD2 in the crystal structure bound to LRP6 E3E4 is also shown (PDB code 3S2K). The expected disulfide bond pattern for Dkk4FL is shown below the sequences, and the locations of CRD1 and CRD2 are also indicated. B, the absolute combined 1HN and 15NH secondary chemical shifts for Dkk4FL determined by calculating the difference between the observed and predicted random coil chemical shift values for each residue. A schematic of the domain architecture is shown above, indicating the positions of CRD1 and CRD2. C, heteronuclear 15N{1H}-NOE values determined for Dkk4FL. Error bars, shown in red, indicate an estimate of the error on the measurement. The regular secondary structure predicted by TALOS-N is also indicated above. D, an overlay of 15N/1H TROSY spectra acquired for Dkk4FL (black) and Dkk4N (red).