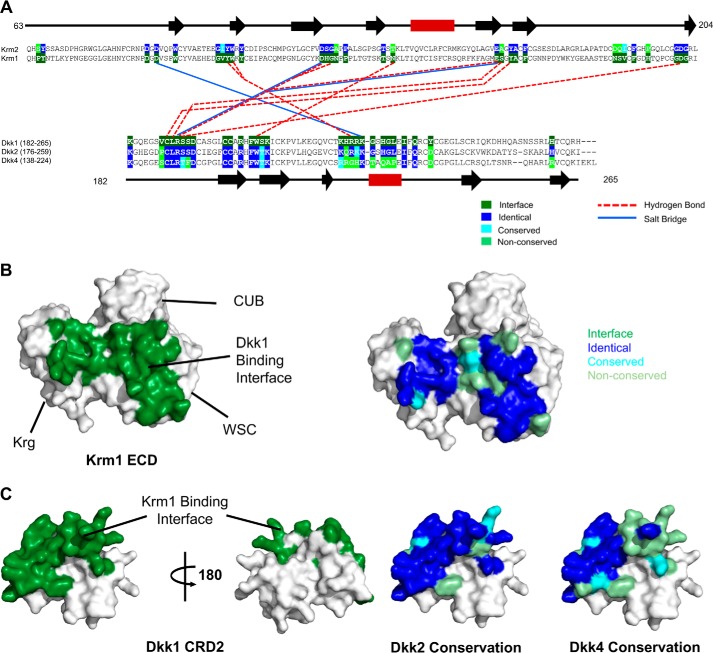
Figure 7.
Analysis of the reported Krm1 ECD and Dkk1 CRD2 interaction sites. A, summary of the key hydrogen bond and salt bridge interactions implied by the Krm1 ECD and Dkk1 CRD2 interface observed in the low resolution crystal structure of the ternary complex (PDB code 5FWW). The complex features an extensive contact surface between the two proteins (1025 and 934 Å2 on Dkk1 CRD2 and Krm1 ECD, respectively), involving many van der Waals interactions. The multiple-sequence alignments shown for Krm1 and Krm2 ECD (top) and Dkk1, Dkk2, and Dkk4 CRD2 (bottom) indicate the high conservation of the binding interface between the two families of proteins. A schematic of the regular secondary structure, as seen in the crystal structure, is displayed above and below the sequence alignments with black arrows and red rectangles representing β-sheets and α-helices, respectively. B, surface views of the Krm1 ECD crystal structure (PDB code 5FWW) showing the location of the Dkk1 CRD2-binding site (left panel, highlighted in green) and conservation of the Krm1 residues in Krm2 at the Dkk1 CRD2-binding interface (right panel). C, surface views of the crystal structure of Dkk1 CRD2 (PDB code 5FWW) showing the location of the Krm1 ECD binding site (left panels, highlighted in green) and the sequence conservation of Dkk2 and Dkk4 residues at the Krm1 ECD binding interface (right panel).