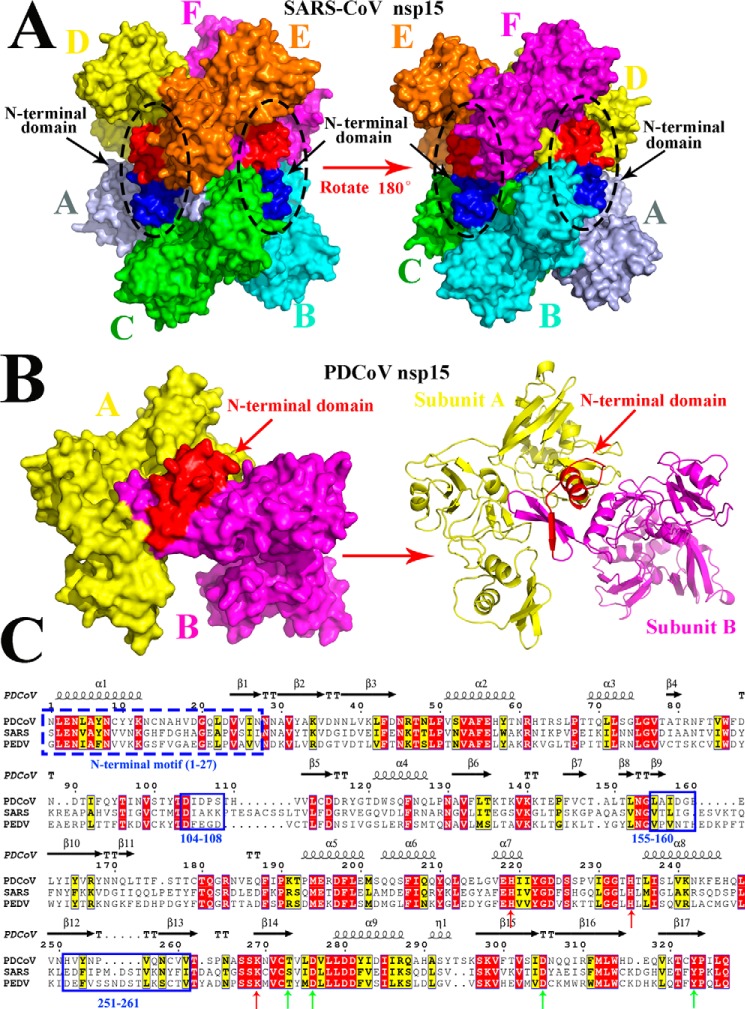
Figure 3.
Predicted residues involved in the dimerization of PDCoV nsp15 determined by sequence and structural alignments. A, structure of SARS-CoV nsp15 (PDB code 2rhb) is a homohexamer with six monomers A (light blue), B (cyan), C (green), D (yellow), E (orange), and F (magenta), and three NTDs are shown in red, and the other three NTDs are shown in blue and are indicated by black arrows. B, predicted three-dimensional structure of PDCoV nsp15 that was built in the SWISS MODEL website. Monomer A (yellow) and monomer B (magenta) form a dimer via the interaction with the N-terminal domain (red), and the right panel is the cartoon formation of PDCoV nsp15 depicted in PyMOL. Monomer A (yellow) and monomer B (magenta) interact with each other through the NTD (red) that are indicated by red arrows. C, amino acid sequence alignment of PDCoV, SARS-CoV, and PDCoV nsp15s. The formal 27 amino acids of these two nsp15s are depicted with a blue dotted line; Asp-104 to Ser-108, Leu-155 to Glu-160, and His-251 to Val-261 residues on PDCoV nsp15 are depicted with the blue solid lines. The conservative sites of three catalytic sites and four binding sites are indicated with red and green arrows, respectively.