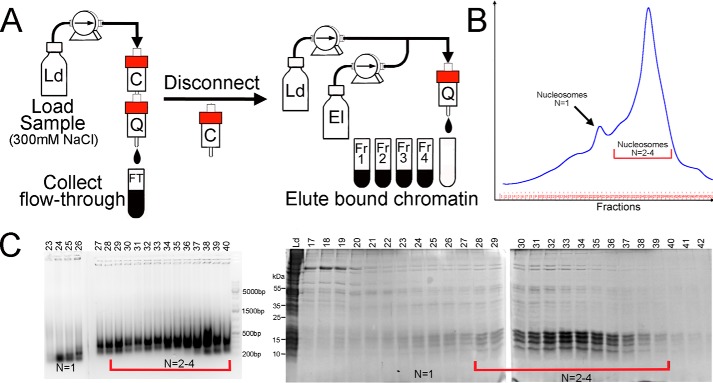
Figure 3.
The details of the column chromatography step used for chromatin purification. A, fragmented and salt-extracted chromatin (Fig. 1) is loaded on the tandem carboxymethyl (C) and quaternary amine (Q) column using loading buffer (Ld). The cation-exchange column traps impurities and is disconnected before Q elution. B, UV (280 nm) elution diagram of the Q anion-exchange column. The column was eluted (El) using a linear salt gradient as described under “Experimental procedures.” C, fractions were analyzed by agarose gel DNA electrophoresis (ethidium bromide staining) (left) and SDS-PAGE (right). Mononucleosomes elute first, followed by oligonucleosomes near the end of the gradient. The highest purity is achieved for larger chromatin fragments, underscoring the importance of controlled and specific chromatin fragmentation. N, the predominant oligomeric form present (e.g. N = 1 = mononucleosome).