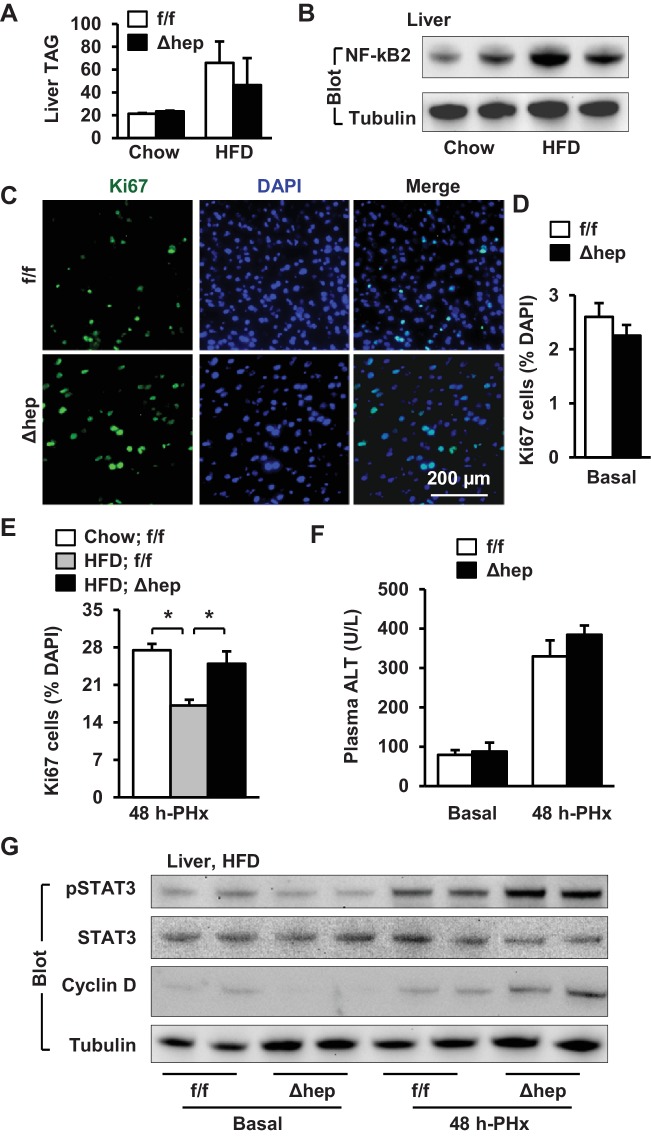
Figure 7. Hepatic NIK deficiency corrects impaired hepatocyte reparative proliferation in mice with NAFLD.
(A–B) C57BL/6 males (8 weeks) were fed a normal chow diet (n = 5) or a HFD (n = 5) for 10 weeks. (A) Liver TAG levels (normalized to liver weight). (B) NF-kB2 p52 in liver extracts was immunoblotted with anti-NF-kB2 antibody (normalized to α-tubulin levels). (C–H) NIKf/f and NIKΔhep males were fed a HFD for 10 weeks followed by PHx, and livers were harvested 48 hr after PHx. (C) Representative immunostaining of liver sections with anti-Ki67 antibody. (D) Baseline Ki67+ cell number in resected liver sections obtained from PHx. NIKf/f: n = 4, NIKΔhep: n = 4. (E) Liver Ki67+ cell number (normalized to DAPI+ cells). Chow;NIKf/f: n = 3, HFD;NIKf/f: n = 5, HFD; NIKΔhep: n = 4. (F) Plasma ALT levels. NIKf/f: n = 3, NIKΔhep: n = 4. (G) Liver extracts were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Data were statistically analyzed with two-tailed Student’s t test, and presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05.