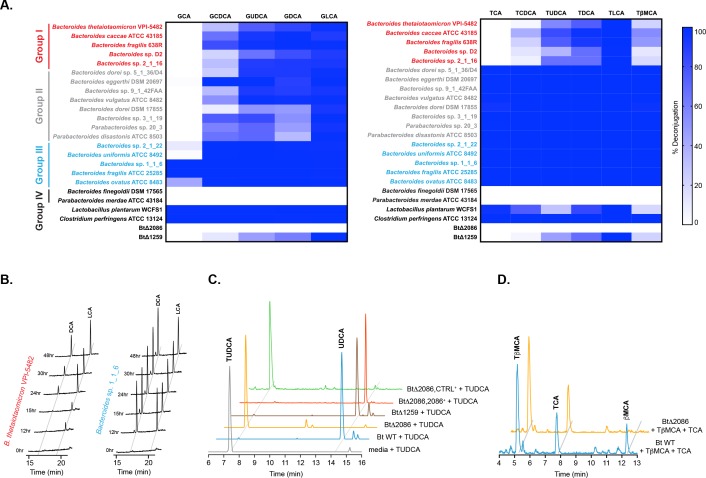
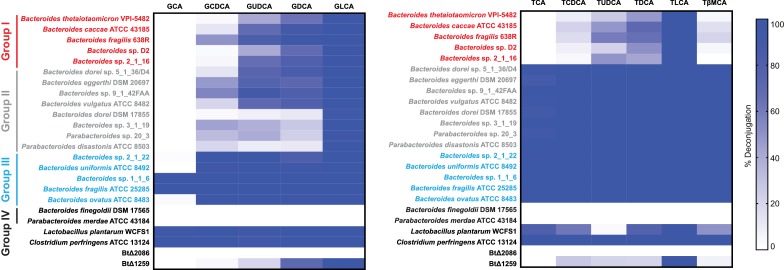
Figure 2. Identification of selective BSH activity in the human gut bacterial phylum Bacteroidetes.
(A) Deconjugation ability of twenty prevalent Bacteroidetes strains and two Firmicutes strains found in the human gut represented as heat maps. Individual strains were incubated for 48 hr total with a group of glyco- or tauro-conjugated bile acids found in human and murine GI tracts. G (glyco-), T (tauro-), CA (cholic acid), CDCA (chenodeoxycholic acid), UDCA (ursodeoxycholic acid), DCA (deoxycholic acid), LCA (lithocholic acid), βMCA (β-muricholic acid). Assays were performed in biological duplicate. Group I (red): Bacteroidetes species that deconjugate primary bile acids based on steroidal core structure (C12 = H but not C12 = OH); Group II (gray): species that deconjugate based on amino acid conjugate; Group III (blue): species that deconjugate all bile acid substrates; Group IV (black): no deconjugation observed. (B) Representative UPLC-MS timecourses for deconjugation of TDCA and TLCA showing that steady state has been reached by 48 hr. (C) Representative UPLC-MS traces showing that Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron wild-type (Bt WT) and BtΔ1259 deconjugate TUDCA, whereas BtΔ2086 does not. BtΔ2086,2086 + recovered the deconjugation function while the BtΔ2086,CTRL +control strain containing an empty pNBU2 vector did not, demonstrating that BT2086 is responsible for bile salt hydrolase activity in Bt. (D) Representative UPLC-MS traces showing that Bt WT deconjugates the murine primary bile acid TβMCA but not TCA, whereas BTΔ2086 (Bt KO) does not deconjugate either bile acid.