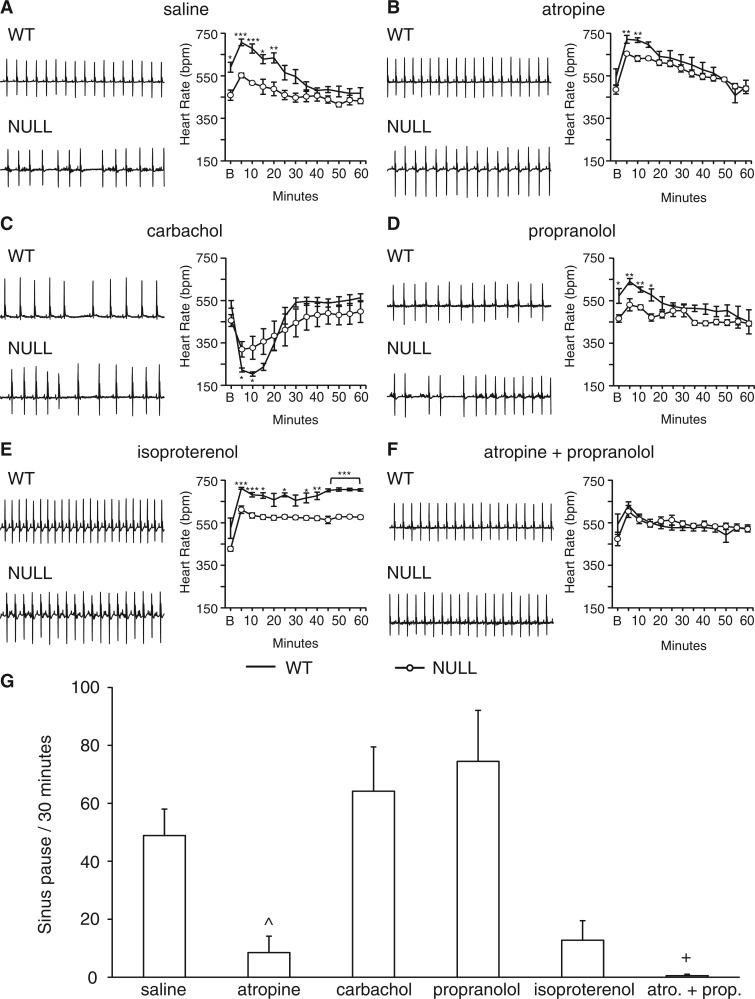
Figure 4.
Atropine improves heart rate and sinus pauses in NULL mice. Mice were treated acutely with pharmacological agents that activate or inhibit the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system. The average heart rate response was binned in 5 min intervals and recorded over a 1-h period. Representative 2 s ECG signals and heart rate response plotted over a 1-h period in both male NULL and wild-type mice after injected with saline (A), 1 mg/kg atropine (B), 0.5 mg/kg carbachol (C), 4mg/kg propranolol (D), 3.3 mg/kg isoproterenol (E), 4 mg/kg propranolol + 1 mg/kg atropine (F). The effect on sinus pauses was quantified over a 30-min period post injection to characterize the change in number of sinus pauses after injection with these drugs or saline (G). Data presented as mean ± SEM. WT mice n = 5 per treatment and NULL mice 4–6 per treatment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.01; NULL saline vs. NULL atropine ^ < 0.05; NULL saline vs. NULL atropine and propranolol + <0.01.