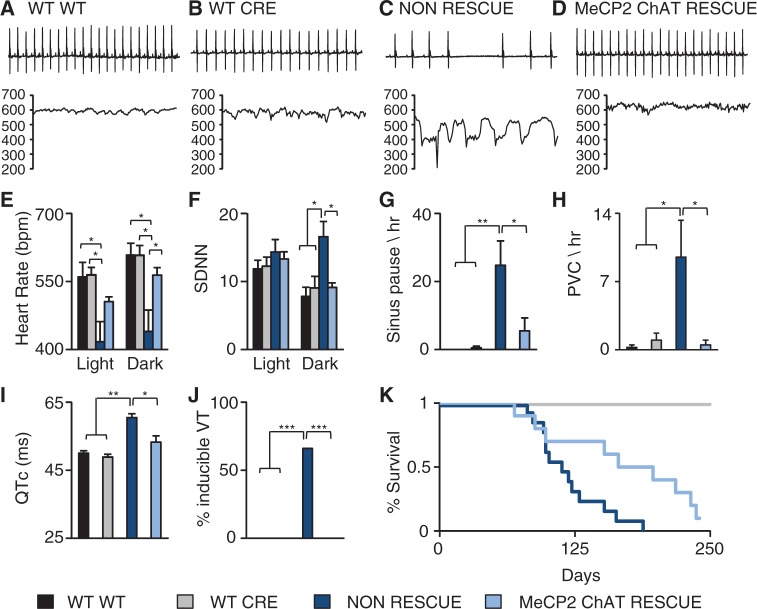
Figure 6.
Restoration of MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons rescues cardiac dysfunction. Telemetry recordings were collected from WT (Mecp2+/Y: No-Cre), CRE (Mecp2+/Y: ChAT-Cre), non-rescue (Mecp2TM2Bird/Y: No-Cre) and MeCP2 cholinergic neuron specific rescue (MeCP2 ChAT rescue, Mecp2TM2Bird/Y: ChAT-Cre) mice. Data from 24-h recording were binned into light and dark cycles and compared to controls. (A-B) Representative 2s ECG trace from a WT and CRE mice and its corresponding 15s instantaneous heart rate showed a normal heart rate. (C) Representative 2s ECG trace from a non-rescue mouse and its corresponding 15s instantaneous heart rate showed an irregular heart rate. (D) Representative 2s ECG trace from a MeCP2 ChAT rescue mouse and its corresponding 15s instantaneous heart rate showed a more regular heart rate. (E) Non-rescue mice had decreased heart rate during the light and dark cycle and the decreased heart rate was rescued in MeCP2 ChAT rescue mice during the dark cycle. (F) Restoring MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons normalized the heart rate variability. Restoring MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons was sufficient to rescue the incidence of sinus pauses (G) and PVCs (H). (I) Non-rescue mice had a prolonged QTc which is rescued in the MeCP2 ChAT rescue. (J) Non-rescue mice had a high incidence of inducible arrhythmias that is rescued in MeCP2 ChAT rescue. (K) Restoring MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons improved survival outcome. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; Telemetry: WT n = 4, CRE n = 4, non-rescue n = 5, MeCP2 ChAT rescue n = 5; ECG and PES: WT n = 3, CRE n = 4, non-rescue n = 6, MeCP2 ChAT rescue n = 6; Survival: WT n = 10, CRE n = 13, non-rescue n = 13, MeCP2 ChAT rescue n = 10.