Figure 1.
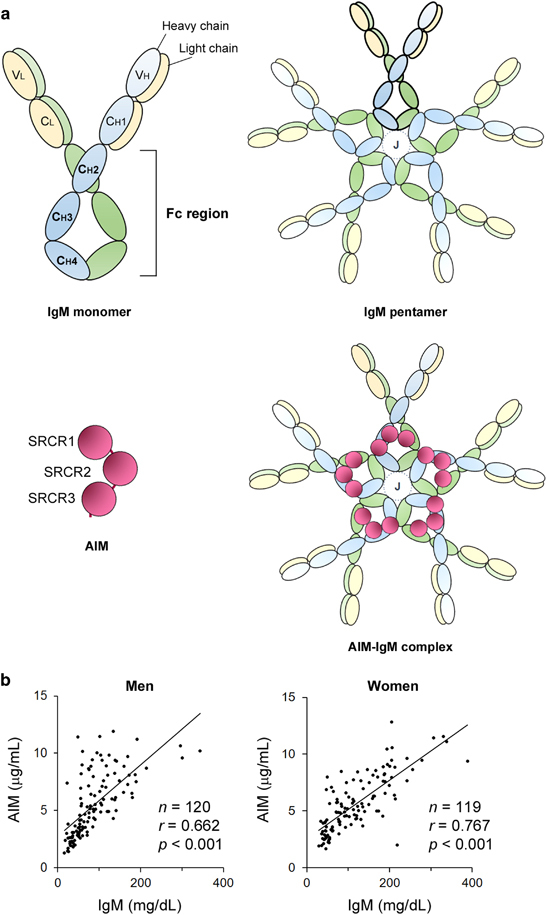
AIM binds to the Fc region of the IgM pentamer in blood. (a) Schematic structures for IgM and AIM. Like other immunoglobulins, such as IgG, the IgM monomer consists of two heavy chains (blue or green) and two light chains (yellow), each of which are covalently connected by disulfide bonds. The immunoglobulin monomer is divided into two regions: a variable region required for recognition of specific antigens and a constant region, which is identical among all the immunoglobulins with the same isotype. The fragment crystallizable (Fc) region is a tail part of the constant region including CH2-CH4 domains and is important for various immunological responses through binding to Fc receptors expressed on the surface of immune cells. Generally, IgM exists as a pentamer in blood. Each IgM monomer is linked by disulfide bonds, and a J chain indispensably joins to this pentameric association. AIM, which harbors three SRCR domains, binds to the Fc region of the IgM pentamer. Although five AIMs may theoretically bind to one IgM pentamer (illustrated as an AIM–IgM complex), it is hypothesized that one or two AIMs associate with an IgM pentamer in blood. (b) A strong correlation in serum levels of AIM and IgM in men (left, n=120, average age 49 years) and in women (right, n=119, average age 49 years) was observed. The data are modified from a previously published report.3
