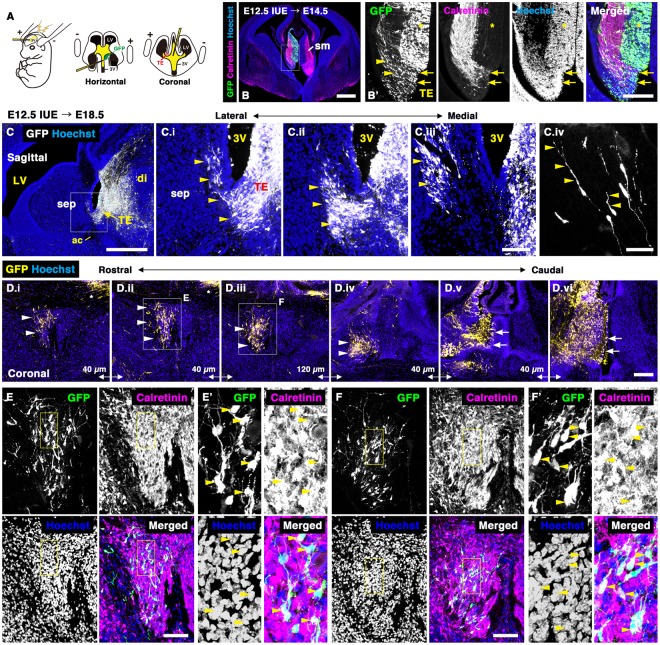
Figure 4.
Thalamic eminence-derived cells undergo rostrodorsal migration into the septal nuclei. (A) Schematic diagram of in utero electroporation (IUE). Plasmid DNA was microinjected into the third ventricle of E12.5 brains and electroporated using a forceps-type electrode. (B) Coronal sections of E14.5 mouse embryos that were electroporated with pCX-GFP at E12.5. TE cells expressing CalR were labeled by GFP (arrows). (C,D) The TE was electroporated with pCX-EGFP at E12.5. The distribution of GFP-positive cells was analyzed in sagittal (C) and coronal (D) sections of E18.5 brains. The boxed area in C is magnified in C.i. C.iv shows migrating GFP-positive cells in the developing septum. D.i-D.vi show rostral (D.i) to caudal (D.vi) coronal sections. Many GFP-positive cells migrated rostrally from the TE to the septum. Arrows indicate the site of electroporation. (E,F) Confocal images of E18.5 brains stained with anti-GFP and anti-CalR antibodies. Boxed areas in E and F are magnified in E’ and F’, respectively. Almost all migrating GFP-positive cells expressed CalR, a marker of the TE (arrowheads). Sections were counterstained with Hoechst 33342. ac, anterior commissure; di, diencephalon; LV, lateral ventricle; sep, septal nuclei; sm, stria medullaris; TE, thalamic eminence; 3 V, third ventricle. Scale bars: 50 µm in C.iv, 100 µm in C.i-iii,E,F, 200 µm in B’,D, and 500 µm in B,C.