Fig. 3.
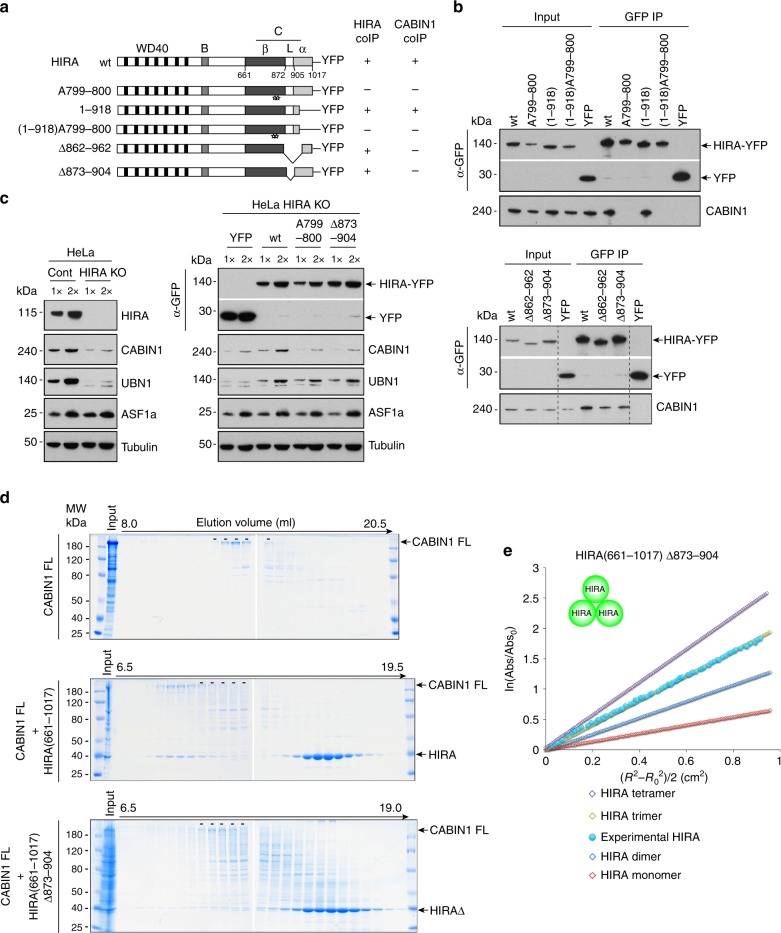
Domains of HIRA involved in its homooligomerization and CABIN1 interaction are distinct. a YFP constructs of human HIRA and mutants. Three different structures matching the previously described C domain are indicated: β-strand (aa 661–872), loop (aa 873–904) and α-helical (aa 905–1017) domains. Star indicates single amino acid substitution with alanine. The co-immunoprecipitation efficiency of endogenous CABIN1 (CABIN1 coIP) is indicated for each construct, “+” indicates that the efficiency of coIP is similar to the one obtained with the wt HIRA construct and “−” indicates that the efficiency of the coIP is decreased. b Western blot analysis of anti-GFP-immunoprecipitates from U2OS nuclear extracts expressing YFP-tagged proteins. Input corresponds to 10% of nuclear extract used for each experiment. c (Left) Western blot analysis of nuclear extracts from HIRA KO and control HeLa cells. (Right) Western blot analysis of nuclear extracts from HeLa HIRA KO cells expressing YFP-tagged proteins. d Superose 6 fractionation of recombinant proteins CABIN1 FL, CABIN1 FL + HIRA(661–1017) and CABIN1 FL + HIRA(661–1017) Δ873–904. The dashes indicate the fractions in which free CABIN1 FL elutes. Input corresponds to protein at the concentration that it was loaded onto the Superose 6 column. e Equilibrium sedimentation of recombinant protein HIRA(661–1017) Δ873–904. Theoretical (open symbols) and experimental (closed symbol) curves are shown