Figure 4.
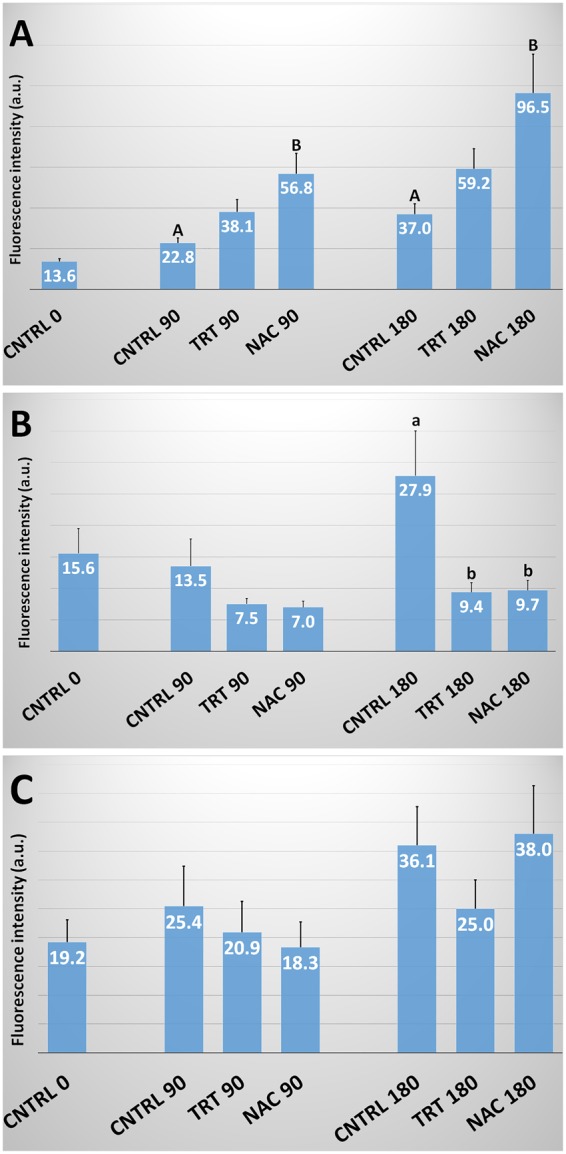
H2DCFDA-detected ROS in human, bovine and ascidian spermatozoa exposed to metabolic enhancers. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) detected by H2DCFDA in human (A), bovine (B) and ascidian (C) sperm divided in three groups treated with: (1) five metabolic enhancers (vitamins B6 and B12, 5 methyl THF, zinc and N-acetyl cysteine) (TRT group); (2) n-acetyl-cysteine (NAC group); and (3) medium alone (CNTRL group). Mean (±SE) values of ROS were evaluated in H2DCFDA-loaded spermatozoa, arranged in TRT, NAC and CNTRL groups and then incubated for 0, 90 and 180 min. ROS production was calculated by evaluating fluorescence intensity (Fo) at the emission peak (~520 nm). Statistically significant differences between groups for each evaluated time point are expressed as different capital (A vs. B; P < 0.01) and small (a vs. b; P < 0.05) letters.
