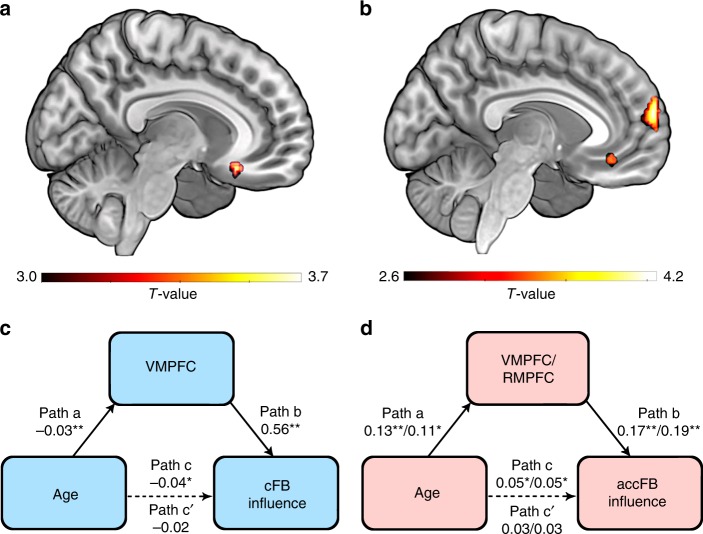
Fig. 3.
Neural mediators of age-related changes in cFB and accFB influence. a Statistical parametric map depicting VMPFC (SVC FWE < 0.05) signals differentiating cFB varying from negative to positive values at the feedback receipt event, which correlated positively with individual differences in the cFB influence (see also Supplementary Table 2). b Statistical parametric map depicting VMPFC (SVC FWE < 0.05) and RMPFC (whole-brain and SVC FWE < 0.05) signals differentiating accFB varying from negative to positive values at the partner-evaluation event, which correlated positively with individual differences in the accFB influence (see also Supplementary Table 2). c Age-related decrease in the cFB influence was mediated by the cFB-related parametric modulation estimates of VMPFC (a) (The numbers indicate regression coefficients. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; Bootstrapping mediation analysis). d Age-related increase in the accFB influence was mediated by the accFB-related parametric modulation estimates of VMPFC and RMPFC (b) (Regression coefficients before and after the slash correspond to VMPFC and RMPFC, respectively. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; Bootstrapping mediation analysis)