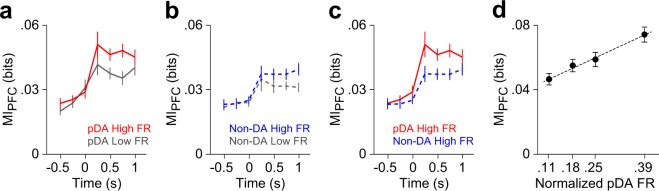
Figure 4.
VTA-driven modulation of information in the PFC. (a,b) MI between pairs of PFC neurons and stimulus were computed for trials with high and low VTA activity, based on the mean firing rate (FR) of pDA and non-DA neurons measured during the duration of tone presentation. MI in the PFC is higher for trials with high FR than with low FR activity of pDA neurons (a; n = 159 pairs, p < 0.05, Sign test). In contrast, PFC MI values are similar across trials with high and low FR of Non-DA neurons (b; n = 159 pairs, p = 0.3, Sign test). (c) MI analyses for trials limited to high FR VTA activity revealed that PFC MI values are maximized by pDA rather than by non-DA neurons (n = 159 pairs of neuron, p < 0.05, Sign test at +0.5 s). (d) MI values in the PFC increased proportionally to the normalized FR activity of pDA neurons (MI computed at +0.5 s, ρ = 0.2, p < 1.10−6, Pearson correlation, N = 151 pairs × 4 quarters; dashed line shows linear least square fitting). In all panels mean ± s.e.m. is shown.