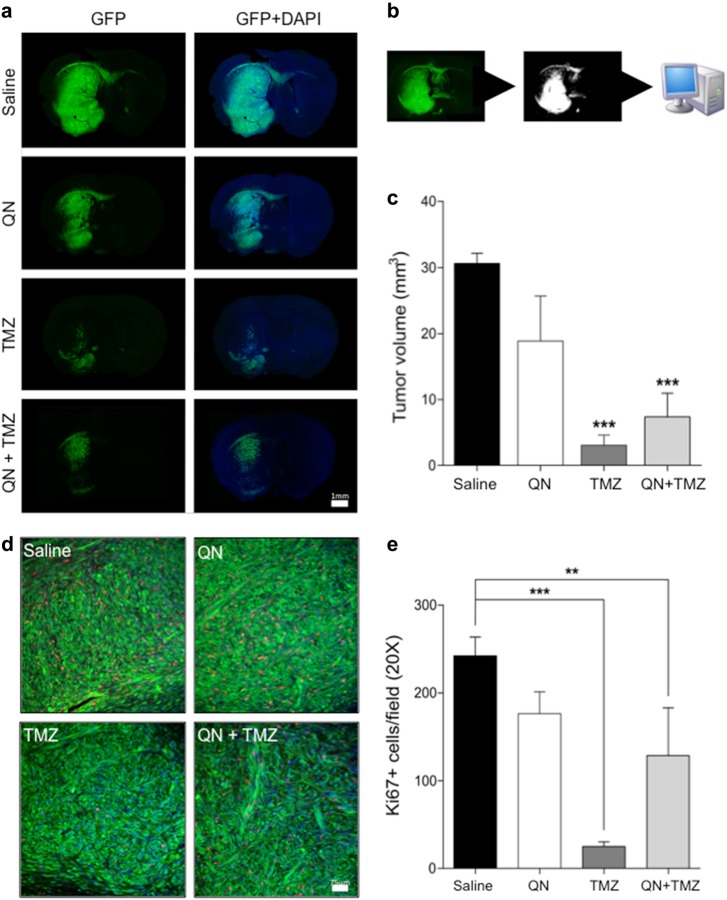
Fig. 8. In vivo effect of TMZ and QN, alone or in association, on the growth of GSC#1 brain xenografts.
Effects of QN, TMZ, and combined TMZ plus QN on the growth of intracerebral GFP-expressing GSC#1 xenografts. a Photomontages of representative coronal sections of the mouse brain illustrating the site of cell injection and brain invasion by 16 weeks after grafting. Saline-treated control mice developed large infiltrating tumors in the brain hemisphere homolateral to the grafting side. Tumor cells spread contralaterally along the corpus callosum and anterior commissure. Treatment with QN did not change the growth pattern of brain tumors. Conversely, both TMZ-treated mice and mice treated with combined TMZ plus QN harbored smaller tumors with remarkable reduction of brain infiltration in the grafted hemisphere and inter-hemispheric pathways as well. Scale bar, 1 mm. b Schematic drawings showing the method used for automated demarcation of brain infiltration and for calculating the volume of the brain region invaded by the GFP-expressing GSC#1. c Diagrams showing the volume of the brain region invaded by the GFP-expressing GSC#1 (***p < 0.0001). d Representative immunostaining with Ki67 for assessment of cell proliferation. Scale bar, 75 μm. e Proliferation of tumor cells was significantly reduced both in TMZ-treated mice and mice treated with combined TMZ plus QN (***p < 0.0001; *p < 0.05)