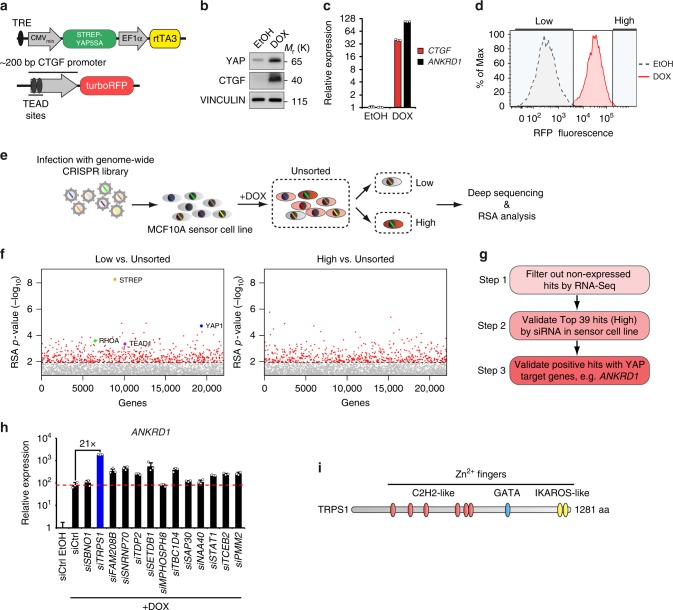
Fig. 1.
Identification of the YAP modulator TRPS1 using a genome-wide CRISPR screen. a Schematic of the YAP activity sensor system. The sensor cell line harbours a doxycycline inducible Strep-YAP5SA allele and a turboRFP (red fluorescent protein) reporter under the control of a CTGF promoter fragment containing TEAD-binding sites. b Western blot for YAP and CTGF in sensor cells treated with doxycycline (DOX) or ethanol (EtOH). Vinculin serves as loading control. c qRT-PCR analysis of the sensor cell line for the YAP target genes CTGF and ANKRD1. The cells were treated with doxycycline (DOX) or ethanol (EtOH). The chart summarizes three biological replicates. Error bars represent s.e.m. d Flow cytometry for RFP in the sensor cell line after treatment with doxycycline (DOX) or ethanol (EtOH), respectively. e Schematic of the CRISPR screening strategy. MCF10A sensor cells were infected with the genome-wide lentiviral GeCKO v2 CRISPR library. After doxycycline (DOX) treatment, cells were sorted into two subpopulations, “high” or “low”, representing 1% of the cells with highest or lowest RFP signal, respectively. Both populations were then analyzed by deep sequencing to determine the frequency of each sgRNA. f Plots for the distribution of P-values in the low vs. unsorted (left) and high vs. unsorted (right) cells, respectively, after analysis by the redundant siRNA activity (RSA) algorithm. g Workflow for the validation of candidates from the CRISPR screen. h qRT-PCR analysis of ANKRD1 expression in the doxycycline-treated sensor cell line transfected with siCtrl or siRNA targeting candidate YAP modulators. The cells were treated with doxycycline (+DOX) to induce YAP 5SA expression or ethanol (EtOH) as a control. Data presented are means from technical triplicates and error bars represent s.d. i Schematic of the TRPS1 protein