Figure 1.
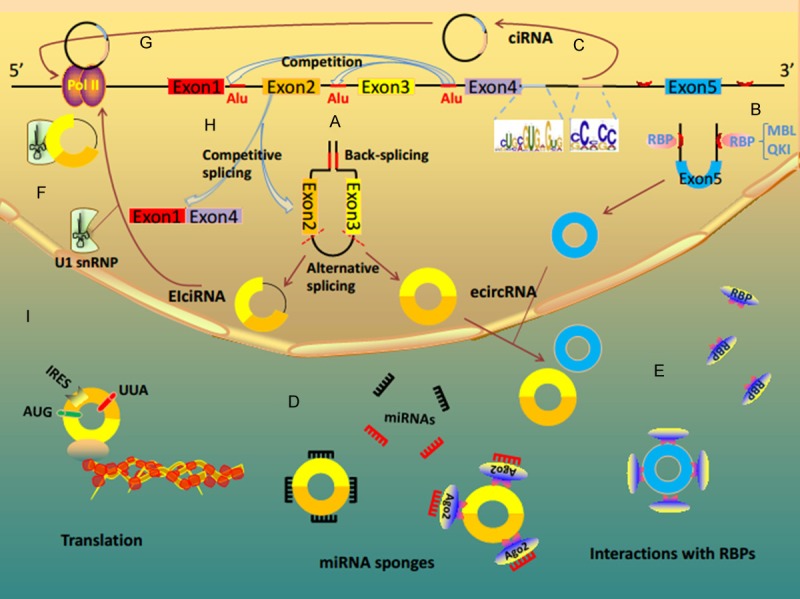
CircRNA biogenesis and function. A. The formation of reversely repeated Alu pairs and the competition between different Alu pairs leading to alternative circularization. During the procession of circularization, pre-mRNAs form ecircRNA or EIciRNA by removing or retaining intron respectively. B. EcircRNA biogenesis can be regulated by RNA-binding proteins, such as MBL and QKI. C. CiRNAs are derived from introns. They depend on a consensus motif containing a 7 nt GU-rich element near the 5’ splice site and an 11 nt C-rich element close to the branchpoint site. D. CircRNAs serve as miRNA sponges to inhibit miRNA activity. E. Some circRNAs function as protein sponges and interact with RNA binding proteins (RBPs). F. Some EIciRNAs regulate Pol II transcription of their parental genes via specific RNA-RNA interaction between U1 snRNA and EIciRNAs. G. Some ciRNAs function as positive regulators of Pol II transcription and play a vital part in the efficient transcription of their parent coding genes. H. CircRNAs can modulate linear splicing by competing for splice sites of pre-mRNA. The formation of circRNA affects the alternative splicing of pre-mRNA, generating circRNA and corresponding linear RNA. I. Some circRNAs have protein-coding capacity and can translate proteins.
