Figure 1.
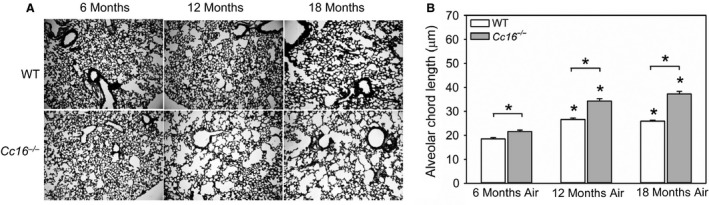
Greater airspace enlargement develops spontaneously in unchallenged Cc16 −/− versus WT mice. (A) Gill's‐stained inflated lungs sections from unchallenged WT versus Cc16 −/− mice at 6, 12, and 18 months of age that are representative of 8–12 mice per group. (B) Images of all well‐inflated microscopic fields of sections of both lung fields (~ten 100× microscopic fields per animal) were captured. Distal airspace size was measured as mean alveolar chord length in WT versus Cc16 −/− mice at 6, 12, or 18 months of age using Scion image software, as described in Methods. The bars show the means and error bars show the SEM values. Data were analyzed using a one‐way ANOVA and pairwise testing was performed using Student’s t‐test. Asterisks indicate P ≤ 0.05 versus air‐exposed mice belonging to the same genotype at 6 months of age, or the group indicated; n = 9–14 mice/group.
