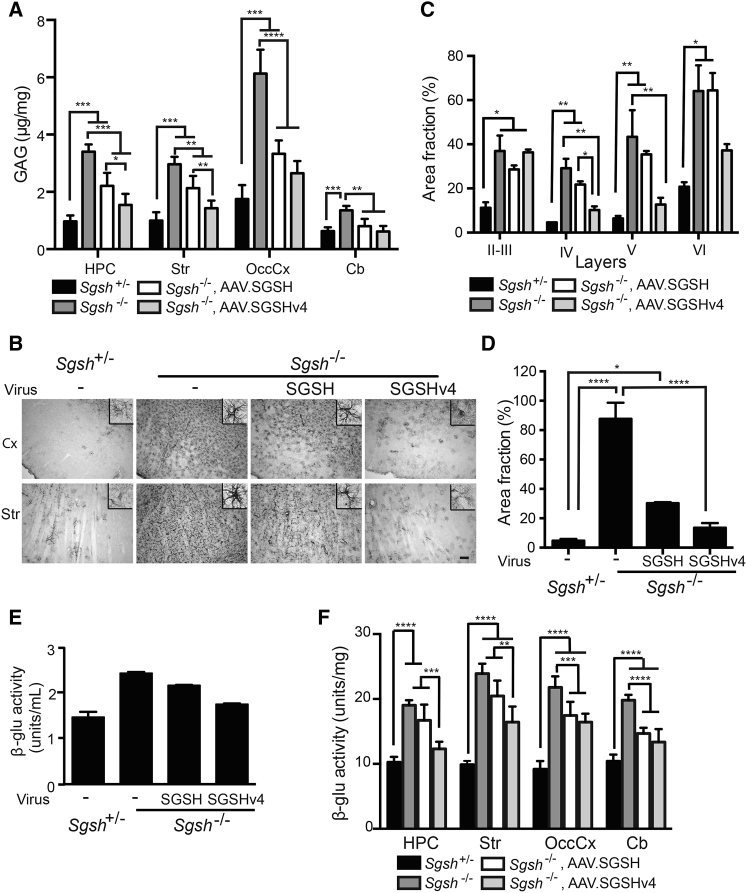
Figure 6.
AAV.SGSHv4 Alleviates Neuropathology in MPS IIIA Mice
Mice (8 wk old) were injected with AAV.SGSH or AAV.SGSHv4 into the lateral ventricle. Animals were euthanized 14 weeks later, and tissues were harvested for analysis of impact on neuropathological readouts. (A) Quantification of GAG in parenchyma from tissues harvested contralateral to the injection site: hippocampus (HPC), striatum (Str), occipital cortex (OccCx), and cerebellum (Cb). n = 4–6. Data represent mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. (B) Glial astrocytosis measured by immunoreactivity for GFAP in sections collected from hemispheres unilateral to the injection site. Representative photomicrographs are from the cortex (Cx) and striatum (Str); n = 3 mice per group, three sections/mouse. Scale bar, 100 μm. Insets show isolated GFAP-immunoreactive glia. (C and D) Threshold image analysis was used to measure the fraction of total area positive for GFAP immunoreactivity in the noted cortical layers (C) and striatum (D). Data represent mean ± SEM, three mice/group and three sections/mouse. For each section, analyses were done on three random fields (100 μm × 100 μm) in the indicated cortical layers and 12 random fields (100 μm × 100 μm) in the striatum. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test. (E and F) β-Glu activity in the CSF and brain tissue lysates after rAAV.SGSH or rAAV.SGSHv4 delivery. (E) β-Glu activity in CSF pooled from four to six mice. (F) β-Glu activity in brain parenchyma from indicated regions. n = 6. Data are mean ± SD. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.