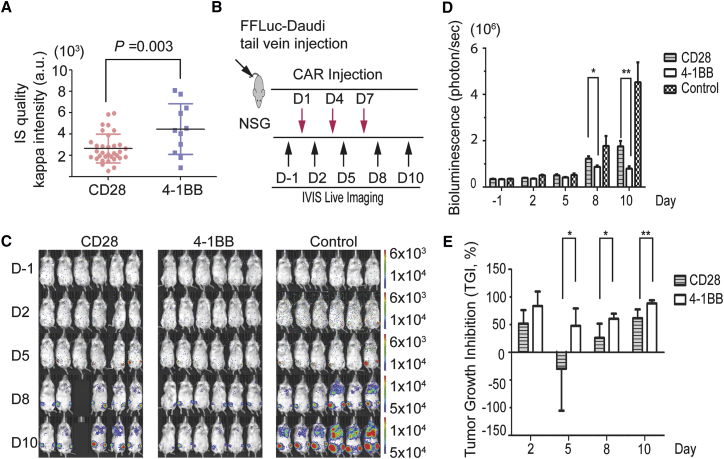
Figure 6.
Superior Anti-tumor Activity from 4-1BB- and Kappa-CAR NK-92 Cells in a Lymphoma Xenograft Model
(A) Representative IS quality measured by quantification of Kappa antigen MFI on the glass-supported planar lipid bilayer between CD28-CAR (red) and 4-1BB-CAR (blue). (B) Diagram of the experimental design of the lymphoma xenograft model. NSG mice (n = 6) were i.v. injected with 1 × 106 FFLuc-Daudi cells (Day −7). At day 1, mice were injected (i.v.) with one dose of 1 × 107 effector CAR NK-92 cells (CD28 and 4-1BB) with 2 × 104 IU of IL-2, and the control group was injected with 2 × 104 IU of IL-2 in PBS. At days 4 and 7, mice were injected with CAR-NK-92 cells with IL-2. (C) Representative images of the tumor burden at the indicated time points. The fluorescence intensity range is displayed (right). (D) Quantification of the tumor burden. Mice were imaged at the indicated days to evaluate the tumor burden expressed as bioluminescence (in photons per second). (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test analysis). Tumor growth was quantified via luciferin signal (average light intensity) and plotted. (E) Tumor growth inhibition (TGI, as a percentage) was calculated at the indicated time points. (D and E) Error bars show ± SD.