Figure 1.
Generation and Functional Evaluation of scFvmVCAM-1, miR-126 Constructs, and TargMB
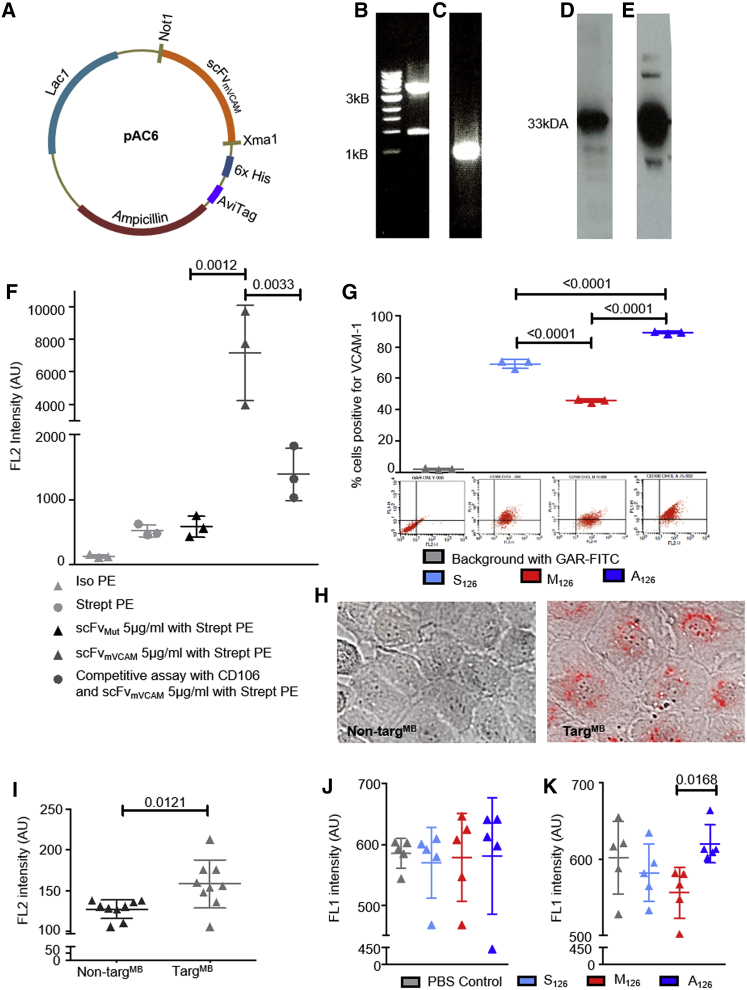
(A) Gene map of scFvmVCAM-1 construct in pAC6 vector. (B) Electrophoresis of pAC6 plasmid (above 3 kB marker) after restriction digest is shown; successful enzymatic digestion is observed with visualization of 1-kB cut out. (C) Electrophoresis of scFvmVCAM-1 (around 1 kB marker) after PCR amplification is shown. (D and E) Western blot analysis (D) shows successful protein purification of scFvmVCAM-1 demonstrated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-coupled anti-6× His-tag antibody, and in vivo biotinylation of scFvmVCAM-1 (E) demonstrated with streptavidin-HRP; both western blots show bands around 33 kDa. (F) Functionality of scFvmVCAM-1 and efficiency of in vivo biotinylation were evaluated with R-phycoerythrin streptavidin via flow cytometry; specificity of scFvmVCAM-1 (5 μg/mL)-targeting VCAM-1 was demonstrated in a competitive assay, using commercially available CD106 and scFvmVCAM-1 (n = 3). (G) Flow cytometry assays evaluated effect of miR-126 constructs on VCAM-1 expression; assays demonstrate increased VCAM-1 expression on SVEC4-10 cells after transfection with A126 and decreased expression with M126 as compared to those with S126 (n = 3). Representative flow cytometry dot plots are shown below each bar graph. (H) Representative images show successful transfection of miR-126 using TargMB via microscopy using bright field and TRITC fluorescence channel; scale bar = 10 μm. (I) Flow cytometry analysis detected Cy3 (on miR) after transfection into SVEC4-10 cells (n = 9). (J) Flow cytometry assays show no change in VCAM-1 expression when non-TargMB was used for transfection of miR-126. (K) Flow cytometry assays show decreased expression of VCAM-1 after transfection with TargMB-M126 as compared to TargMB-A126 (n = 5); assays with two groups were analyzed using Student’s t tests and those with more than two groups with equal numbers using repeated-measures one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post tests.