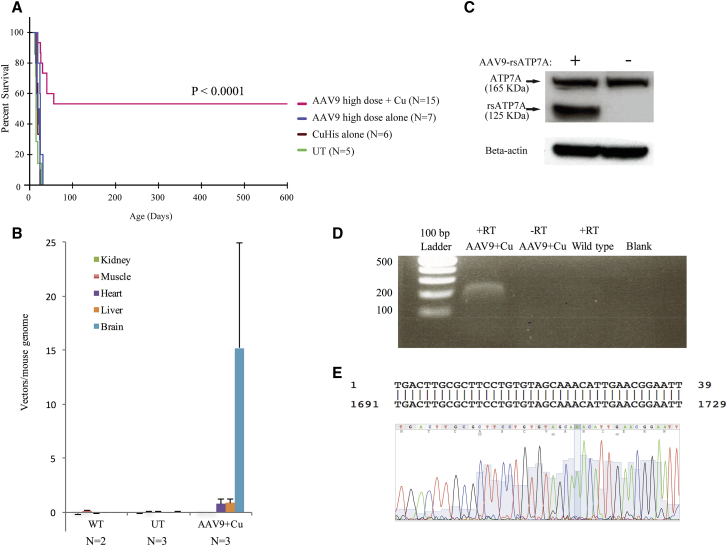
Figure 3.
Results of Cerebrospinal Fluid-Directed rAAV9-rsATP7A Plus sc Copper Histidinate versus Individual Treatments
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve demonstrates superior survival with high-dose AAV9-rsATP7A plus sc copper histidinate (magenta) in comparison to untreated mutants (UT), rAAV9-rsATP7A alone (blue), and sc copper histidinate alone (brown) did not significantly enhance survival beyond that in untreated mutants (green) (p < 0.0001). (B) Viral genome quantification using real-time PCR to detect rsATP7A transgene in mo-br brain DNA after administration of 1.6 × 1010 viral particles of either AAV. Non-injected mutant (UT) and wild-type (WT) controls also shown. Error bars, SEM. (C) Western blot of total proteins from high-dose rAAV9-rsATP7A-injected wild-type mouse brain detects recombinant rsATP7A (≈125 kDa) as well as endogenous full-length murine ATP7A (≈165 kDa). Bottom, Beta-actin loading control. (D) Stable long-term expression of rsATP7A 597 days post-administration of 1.6 × 1010vg AAV9-rsATP7A, documented by RT-PCR from brain RNA extracted from a long-term surviving mutant male. −RT refers to a negative control for RT-PCR, with RNA but no reverse transcriptase included in the reaction. (E) Capillary DNA sequencing of the excised band verified that it represented the ATP7A transgene transcript (exon 5). Alignment to Homo sapiens ATP7A, sequence ID, gi|532691751|NM_001282224.1.