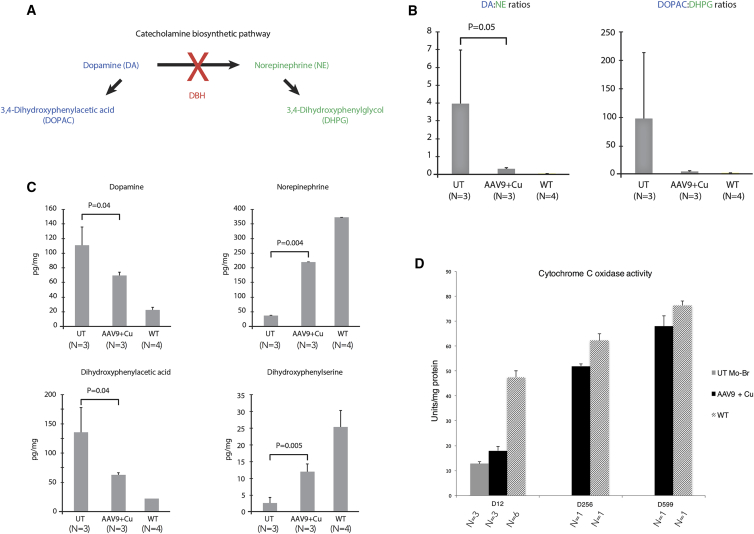
Figure 5.
Brain Neurochemical Measurements in rAAV9-rsATP7A Plus sc Copper Histidinate Combination-Treated mo-br Mice
(A) Summarized version of catecholamine biosynthetic pathway. Dopamine (DA) is converted to norepinephrine (NE) by the copper-dependent enzyme dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH). (B) Markedly increased DA:NE and DOPAC:DHPG ratios in 12-day-old untreated mo-br mutants (UT) compared to mutant mice that received high-dose rAAV9-rsATP7A plus sc copper histidinate. A two-tailed, paired Student’s t test was used to calculate p. Error bars, SEM. Elevated ratios of proximal:distal metabolites in this pathway are sensitive and specific for diagnosing Menkes disease.10, 12, 30 (C) Individual brain neurochemical levels measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Proximal metabolites in the pathway (DA, DOPAC) are significantly lower in 12-day-old mutant mice treated with high-dose rAAV9-rsATP7A plus copper histidinate compared to untreated mutants (UT). Distal metabolites (NE, DHPG) are significantly higher. Two-tailed, paired Student’s t tests were used to calculate p values. Error bars, SEM. (D) Brain cytochrome c oxidase (CCO) activity in untreated mo-br (UT), high-dose rAAV9-rsATP7A plus copper histidinate-treated mo-br (AAV9 + Cu), and wild-type (WT) mice. Note progressive increase in cytochrome c oxidase activity with advancing age in long-term surviving rAAV9 plus sc copper histidinate-treated mutant mice (sacrificed at 256 days and 599 days). Results in the latter four animals reflect triplicate measurements in the four individual brains. Error bars, SEM.