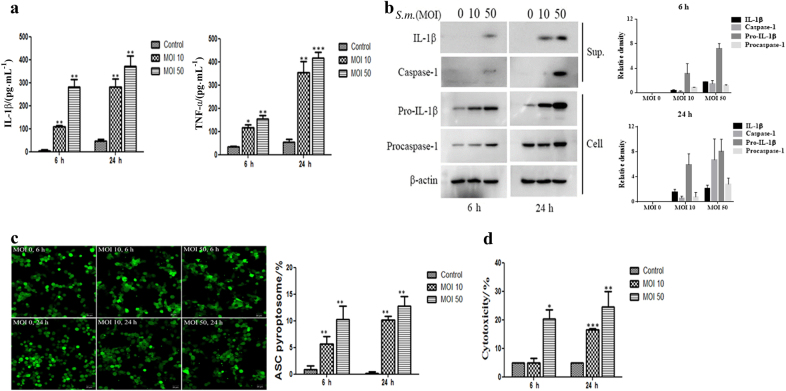
Fig. 1.
S. mutans induces IL-1β secretion and caspase-1 activation, leading to cell death. a THP-1 cells were infected with S. mutans (MOI 10 or 50) for 6 h or 24 h. The cell culture supernatants were assayed for human IL-1β and TNF-α by ELISA. b THP-1 cells were infected with S. mutans (MOI 10 or 50) for 6 or 24 h. IL-1β and caspase-1 secreted into the culture supernatants (sup.) and pro-IL-1β, procaspase-1, and β-actin in the cell lysates (cell) were detected by immunoblotting. The relative western blot band densities were normalised to those of β-actin. c THP-1/ASC-GFP cells infected with S. mutans at each MOI for the indicated times were observed and photographed by fluorescence confocal microscopy (original magnification ×100). The graph in the lower panel shows the percentage of cells containing ASC pyroptosomes. The percentage of cells containing ASC pyroptosomes was calculated as described in the Materials and Methods. d The amount of the cytoplasmic enzyme LDH released into the culture supernatant was measured using an LDH cytotoxicity assay kit. The results represent those from one of three individual experiments. The data are reported as the means ± standard deviations (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. S.m. means S. mutans