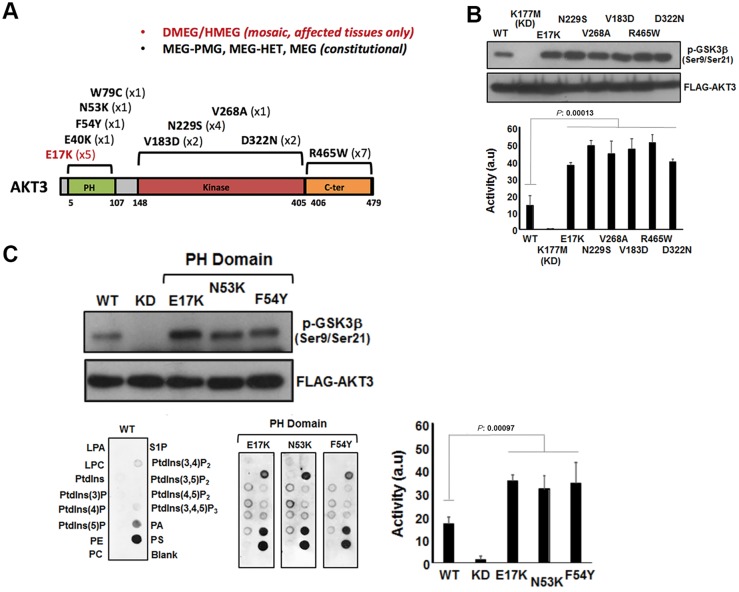
Figure 3.
Analysis of AKT3 activity in vitro. (A) The primary structure of AKT3 showing the relative positions of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain for lipid binding the catalytic kinase domain and C-terminal (C-ter) region. Mutations identified to date are shown along with the numbers of patients with these mutations in brackets. (B) Catalytic kinase domain and C-terminal localizing patient-derived AKT3 mutations are associated with elevated kinase activity. Ectopically expressed wild-type (WT) AKT, a kinase dead variant K177M, the E17K activating pleckstrin homology domain mutant and various patient mutants were assessed for kinase activity using a GSK3β peptide as a substrate in an ex vivo kinase assay. The upper panel shows immune detection of phosphorylated GSK3β peptide following western blotting with anti-phospho-GSK3β (Ser9/Ser21) antibody. The patient mutants all exhibit elevated phospho-activity compared to wild-type. The graph depicts quantitation of phospho-GSK3β (Ser9/Ser21) signal (a.u. = arbitrary units). Error bars represent mean ± SD (n = 4), P-values were determined using Student’s t-test. (C) Pleckstrin homology domain localizing patient mutations are associated with elevated kinase activity and altered phospholipid-binding profile. Left panels show western blot analysis of phospho-GSK3β (Ser9/Ser21) of ectopically expressed wild-type, K177M kinase dead and three pleckstrin homology domain patient mutants; E17K, N53K and F54Y. The graph depicts quantitation of phospho-GSK3β (Ser9/Ser21) signal. Error bars represent mean ± SD (n = 4), P-values were determined using Student’s t-test. The bottom panels depict PIP-membranes seeded with various lipids and phospholipids for dot blot binding analysis. Ectopically expressed FLAG-tagged wild-type and AKT3 pleckstrin homology domain mutants were incubated with the PIP Strips and bound protein detected by western blotting using anti-FLAG. All three pleckstrin homology domain mutants exhibit altered and elevated binding to specific phospholipids compared to wild-type. DMEG = dysplastic megalencephaly; HMEG = hemimegalencephaly; LPA = lysophophatidic acid; LPC = lysophosphocholine; MEG = megalencephaly; P = phosphate; PA = phosphatidic acid; PC = phosphatidylcholine; PE = phosphatidylethanolamine; PMG = polymicrogryria; PS = phosphatidylserine; PtdIns = phosphatidylinositol; S1P = sphingosine-1-phosphate.