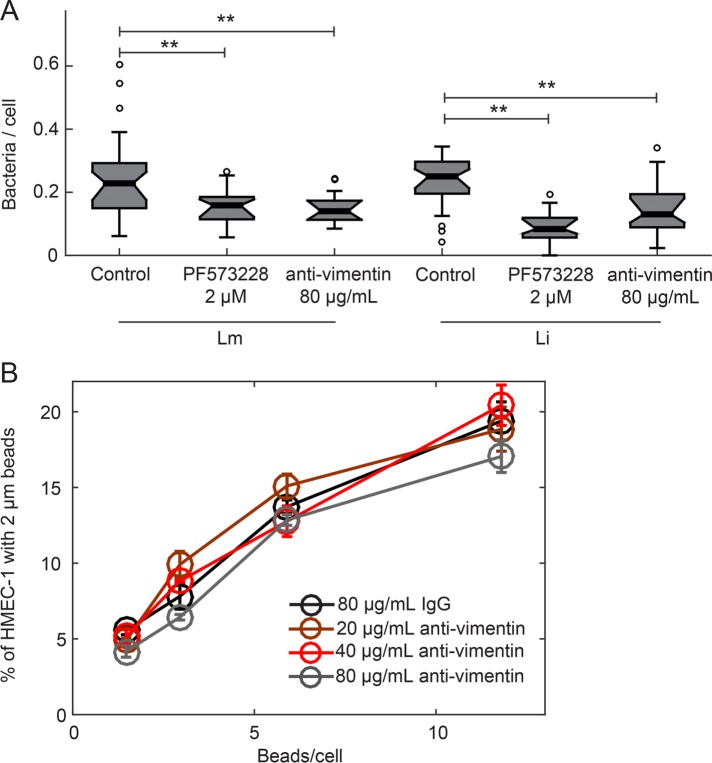
FIGURE 8:
Blocking HMEC-1 with anti-vimentin antibody reduces Li adhesion onto HMEC-1 but not uptake of beads. (A) Boxplots showing the number of bacteria per cell, for HMEC-1 residing on glass substrates and treated with vehicle control, 2 μM PF537228 FAK inhibitor, or 80 μg/ml H-84 anti-vimentin antibody prior to infection. Cells were infected with Lm or Li at an MOI of 4. At 30 min postinfection, samples were fixed and immunostained and adhesion of bacteria was analyzed by microscopy followed by image processing. For each condition, 2300–2600 cells were analyzed in total and data refer to one of two independent experiments. Two asterisks denote statistically significant differences between the median values of control cells vs. all other groups (<0.01; Wilcoxon rank-sum test). (B) HMEC-1 residing on TC polystyrene substrates and blocked for 1 h with various concentrations of H-84 anti-vimentin antibody or isotype control were “infected” with 2 μm beads at different concentrations. The frequency of microbead uptake by HMEC-1 was determined by flow cytometry 2 h post–addition of beads. Plot shows percentage of cells that internalized beads as a function of the beads/cell added for different H-84 antibody concentrations (mean ± SD, N = 4 replicates).