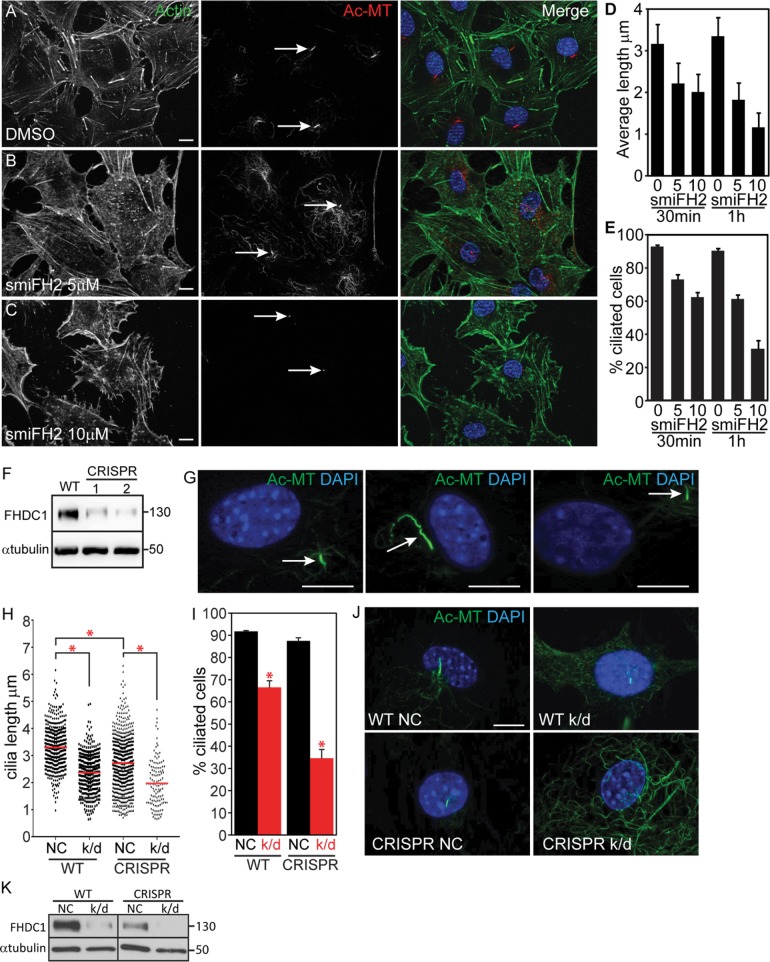
FIGURE 8:
FHDC1 is required for normal cilia assembly. (A–C) NIH 3T3 cells were maintained in low-serum media for 48 h to induce cilia formation. F-actin was detected with phalloidin (green) and cilia were detected with anti-acetylated tubulin (red). Cells treated for 60 min with increasing amounts of smiFH2 lost their cilia in a dose-dependent manner. (D, E) Cells were treated with 0, 5, or 10 μM smiFH2 for 30 and 60 min. Cilia assembly was assessed as in A–C. Both cilia length and the number of cells with cilia were obviously decreased after 30 min of smiFH2 treatment and more so after 60 min. Control cells treated with DMSO (vehicle) maintained their cilia. N = 3, >100 cells counted per experiment. Error bars = SEM. (F) Isolation of two CRISPR lines with diminished levels of FHDC1 expression as determined by immunoblotting. (G) Depletion of FHDC1 results in defective cilia assembly. Partial FHDC1 knockout cells, with diminished levels of FHDC1 expression, are defective for cilia length regulation. These cells frequently exhibit aberrant cilia localization away from the perinuclear region. (H–K) siRNA-mediated knockdown was used to further deplete FHDC1 expression in the partial knockout cell line. NC = negative control; k/d = FHDC1 knockdown. (H–J) Depletion of FHDC1 expression decreases cilia length and reduces the number of ciliated cells following serum starvation. N = 3, >100 cells counted per experiment. Error bars = SEM. * indicates p < 0.0001. (K) FHDC1 was essentially undetectable following siRNA transfection of the partial knockout cells as determined by immunoblotting.