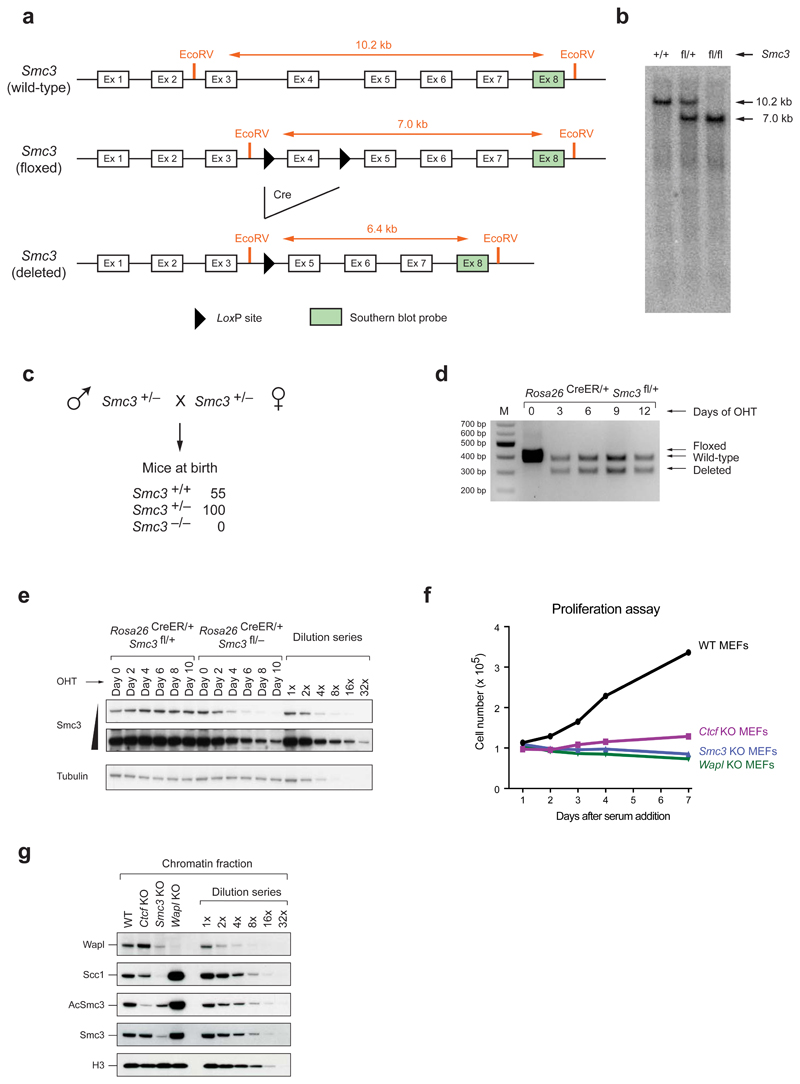
Extended Data Figure 1. Characterization of conditional Smc3 knockout cells.
a, Schematic representation of the wild-type, floxed (fl) and deleted (Δ) Smc3 alleles (after elimination of the neomycin resistance gene). EcoRV fragments, which were used for allele identification by Southern blot analysis with the indicated exon 8 probe, are shown together with their length (in kb). b, Southern blot analysis of tail DNA from wild-type, Smc3fl/+ and Smc3fl/fl mice. c, Absence of Smc3–/– offspring at birth. The genotype of newborn mice from intercrosses of Smc3+/– mice was determined by PCR genotyping. d, Deletion of the floxed Smc3 allele was detected by PCR genotyping in primary Rosa26CreER/+ Smc3fl/+ MEFs at the indicated days after 4-hydroxytamoxifen (OHT) addition. e, The level of Smc3 protein depletion in primary Rosa26CreER/+ Smc3fl/– MEFs was analyzed every second day after OHT addition by immunoblot analysis of whole cell extracts. Control Rosa26CreER/+ Smc3fl/+ MEFs were additionally analyzed together with a dilution series of the day-0 sample. A long and short exposure of the Smc3 immunoblot is shown. f, The efficiency of protein depletion was analyzed by immunoblot analysis of chromatin extracts from starved MEFs at day 10 after OHT treatment (Smc3 and Wapl KO cells) or Adeno-Cre virus infection (Ctcf KO cells). The wild-type chromatin sample was diluted up to 1:32 in order to estimate the relative reduction in protein levels (CTCF: > 4x, Wapl: > 8x and Smc3: > 16x). g, Proliferation capacity of WT MEFs and Ctcf, Smc3 and Wapl KO MEFs. The indicated serum-starved cells were stimulated with 10% fetal calf serum, and cell numbers were measured every day using the Casy counter. All three KO cells failed to respond to proliferate in contrast to wild-type MEFs.