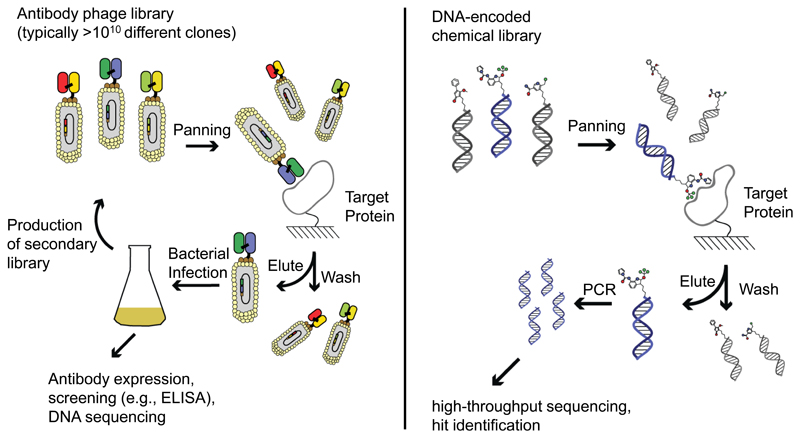
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of biopanning procedures with antibody phage display libraries and with DNA-encoded chemical libraries. In the first case, a large library of phage antibodies is incubated with the target protein of interest, immobilized on a solid support. Selective binders are captured on the affinity support, while the majority of other phage antibodies (which do not bind toia the target) can be washed away. Selected phage particles can be amplified by infecting bacteria, leading to an amplification step and to the generation of more phage particles, which can be submitted to a second round of panning. Alternatively, infected bacteria can be plated onto selective plates and individual colonies correspond to distinct monoclonal antibody clones. Similarly, large collections of organic molecules (individually tagged with DNA barcodes) can be interrogated using an affinity capture procedure. Preferentially enriched molecules can be identified by PCR amplification of the DNA tags, followed by high-throughput DNA sequencing.