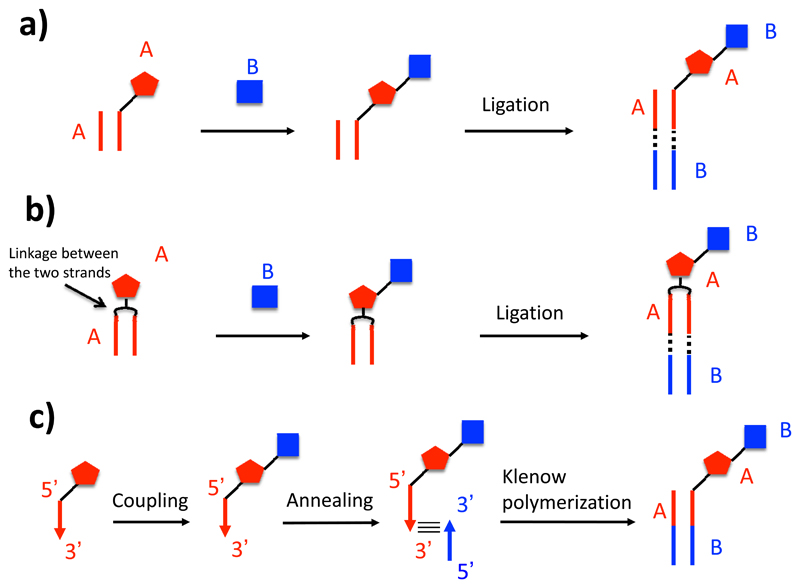
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of encoding strategies for DNA-recorded chemical libraries. (a) In the simplest implementation of this technology, each building block in the synthesis procedure is encoded (i.e., identified) by a distinctive double-stranded DNA fragment. After each chemical reaction, the identity of the newly introduced building block is provided by an additional DNA fragment, which is ligated to the nascent DNA structure. (b) In a variation of the procedure described before, the complementary DNA strands are connected by a linker, which also supports the growth of the nascent molecule. (c) In a different encoding procedure, a first building block is attached at the 5’ end of an oligonucleotide, which contains a suitable identification code. After a second building block has been added to the nascent molecule by chemical reaction, its identity is encoded by the annealing of a partially complementary oligonucleotide, followed by a Klenow polymerization procedure.