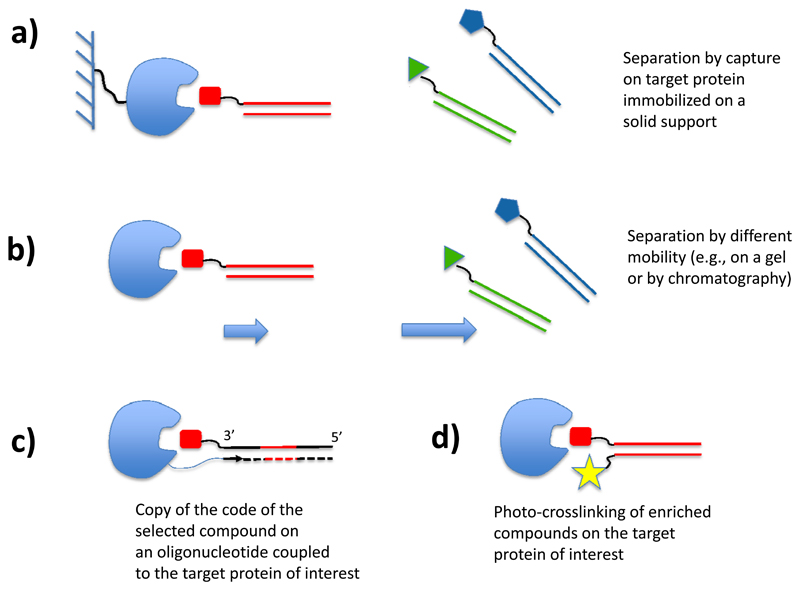
Figure 7.
Selection methods for DNA-encoded chemical libraries. (a) Library members are captured on a target protein, immobilized on a solid support. (b) DNA derivatives, capable of binding to a target protein with sufficient stability in given experimental conditions, are separated from non-binding library members by chromatography or by electrophoresis. (c) Library members encoded by single-stranded DNA molecules, capable of binding to a target protein of interest equipped with a suitable oligonucleotide primer, can be identified by a DNA polymerization step, followed by PCR amplification. (d) Capture of preferentially-binding library members by photo-crosslinking.