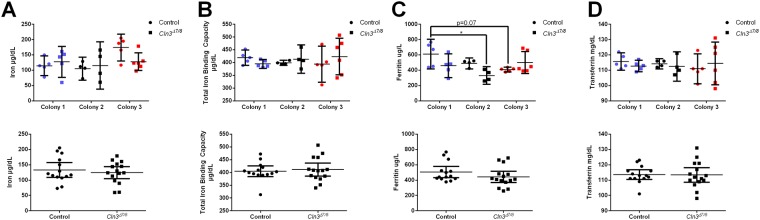
Fig 1. Significant interaction of colony and genotype on ferritin levels between three colonies at 5 months of age.
The basic iron panel values of blood collected from each genotype was analyzed for colonies 1 (blue, Sanford Research), 2 (black, University of Nebraska Medical Center), and 3 (red, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science) for both control (circle) and Cln3Δex7/8 mice (square). Graphs indicate concentration of iron, (A), total iron binding capacity (B), ferritin (C), and transferrin (D), with individual colony data on top and pooled colony data on the bottom. A significant main effect of colony was detected on iron levels, p = 0.0388. (A) A significant interaction between colony and genotype was detected on ferritin levels, p = 0.0249; the colony factor approached significance at p = 0.0677 and the genotype factor had a p-value of 0.0922 (C). Data represented as mean ± 95% CI; data points represent individual mice from indicated colony. Statistical significance for top graphs was determined using ordinary two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test with a Bonferroni correction. Statistical significance for bottom, pooled colony graphs was determined using an unpaired student’s t test. *p<0.05.